DTC P0A3E: IGBT1 temperature too high
DTC P10A8: IGBT2 temperature too high
DTC P10A9: IGBT3 temperature too high
DTC P106B: Condenser temperature too high
DTC P1015: Temperature around CPU too high
DTC P10A8: IGBT2 temperature too high
DTC P10A9: IGBT3 temperature too high
DTC P106B: Condenser temperature too high
DTC P1015: Temperature around CPU too high
MONITOR EXECUTION
- Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC set in memory for the item monitored below)
- Not applicable
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Drive motor IGBT temperature sensor <DTC P0A3E, P10A8, P10A9>
- Drive motor capacitor temperature sensor <DTC P106B>
- Drive motor control module temperature sensor <DTC P1015>
DTC SET CONDITIONS
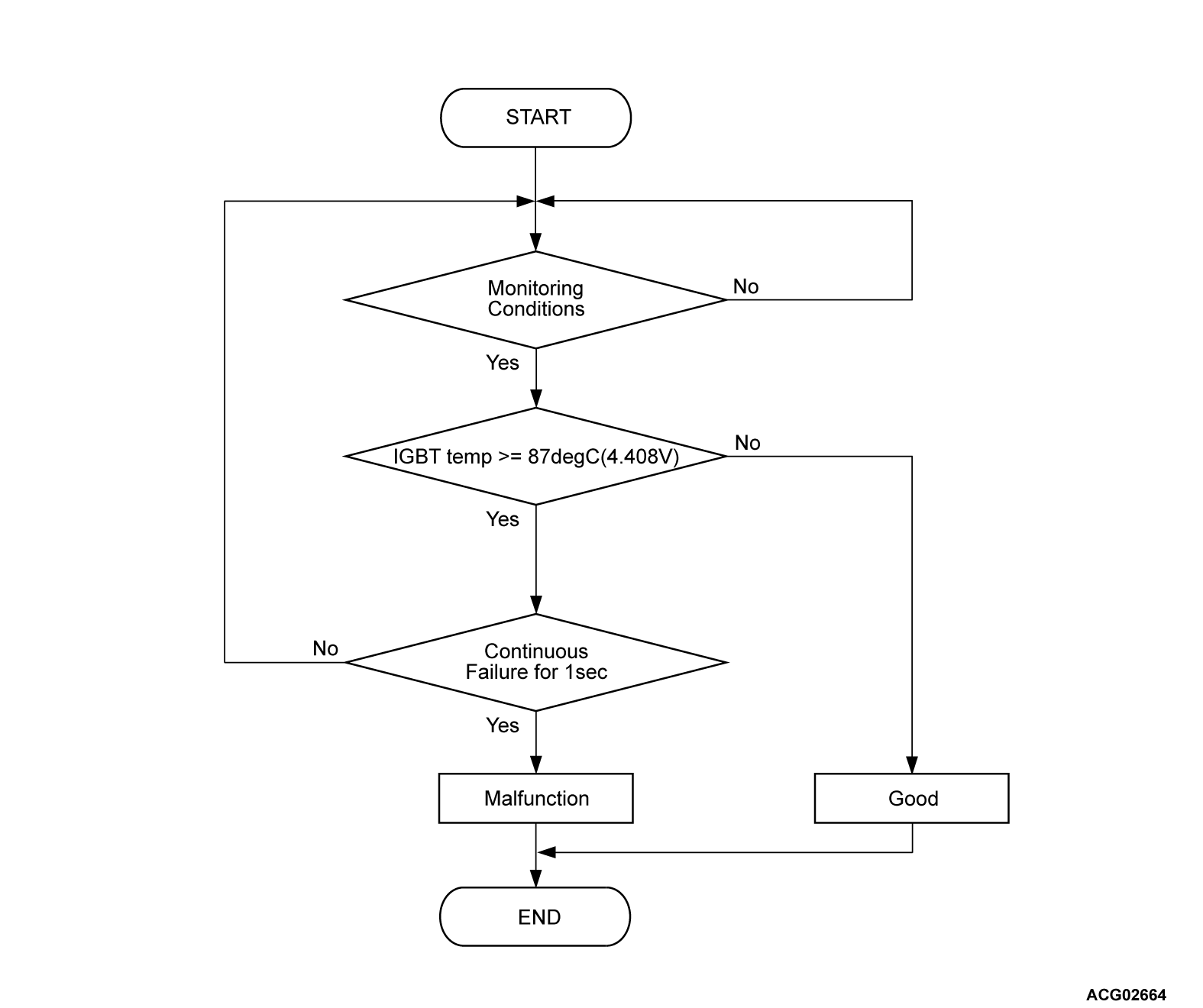
Check Conditions <DTC P0A3E, P10A8, P10A9>
- The vehicle status is propulsion system active.
- Time after above conditions satisfy is more than 10 seconds.
Judgment Criterion <DTC P0A3E, P10A8, P10A9>
- Change of the IGBT temperature is more than 87°C (189°F) (4.408 volts) for 1 second.
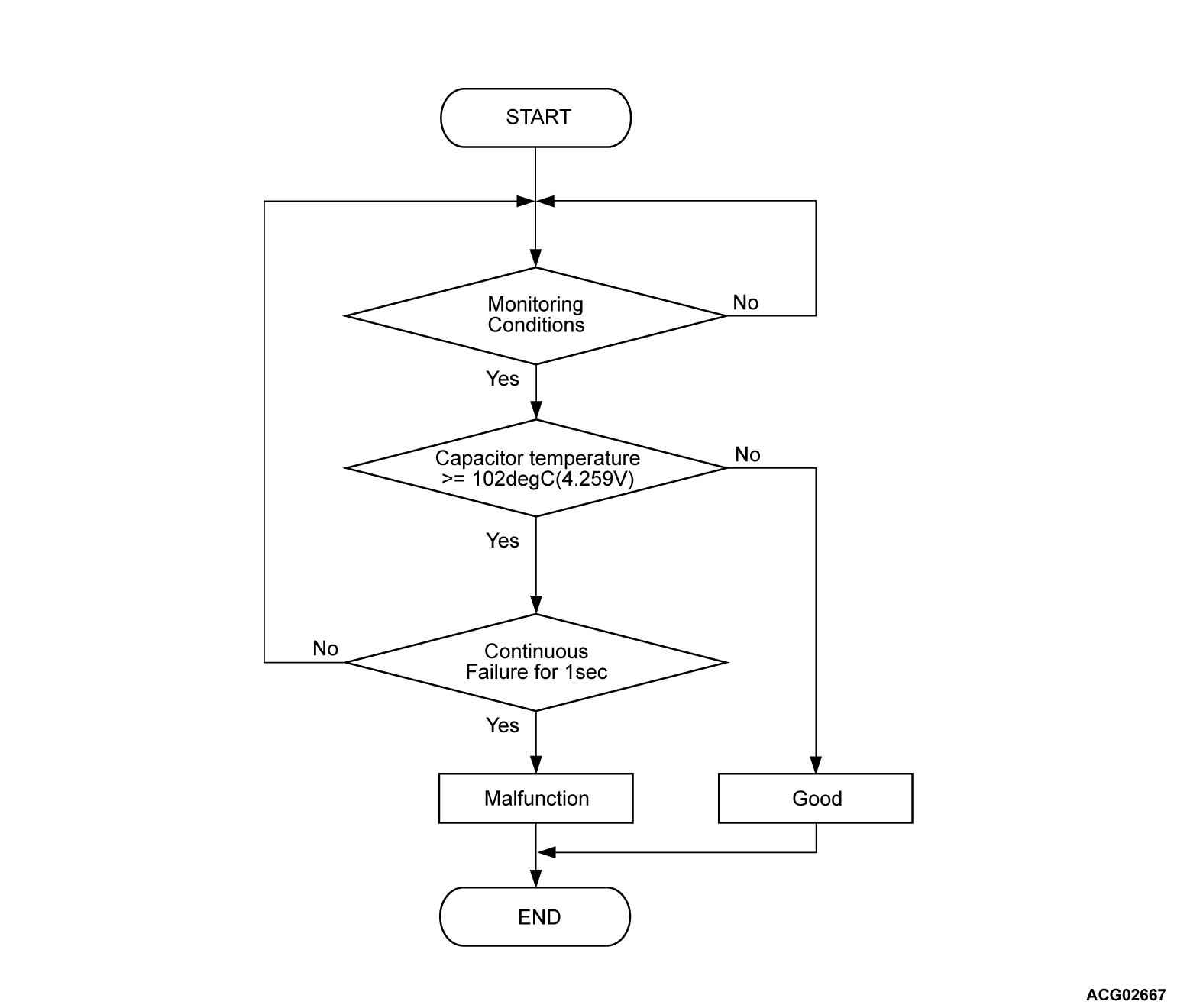
Check Conditions <DTC P106B>
- Power drive unit (GCU) power supply voltage is 8 volts to 16 volts.
Judgment Criterion <DTC P106B>
- Change of the power drive unit (GCU) capacitor temperature sensor temperature is more than 102°C (216°F) (4.259 volts) for 1 second.
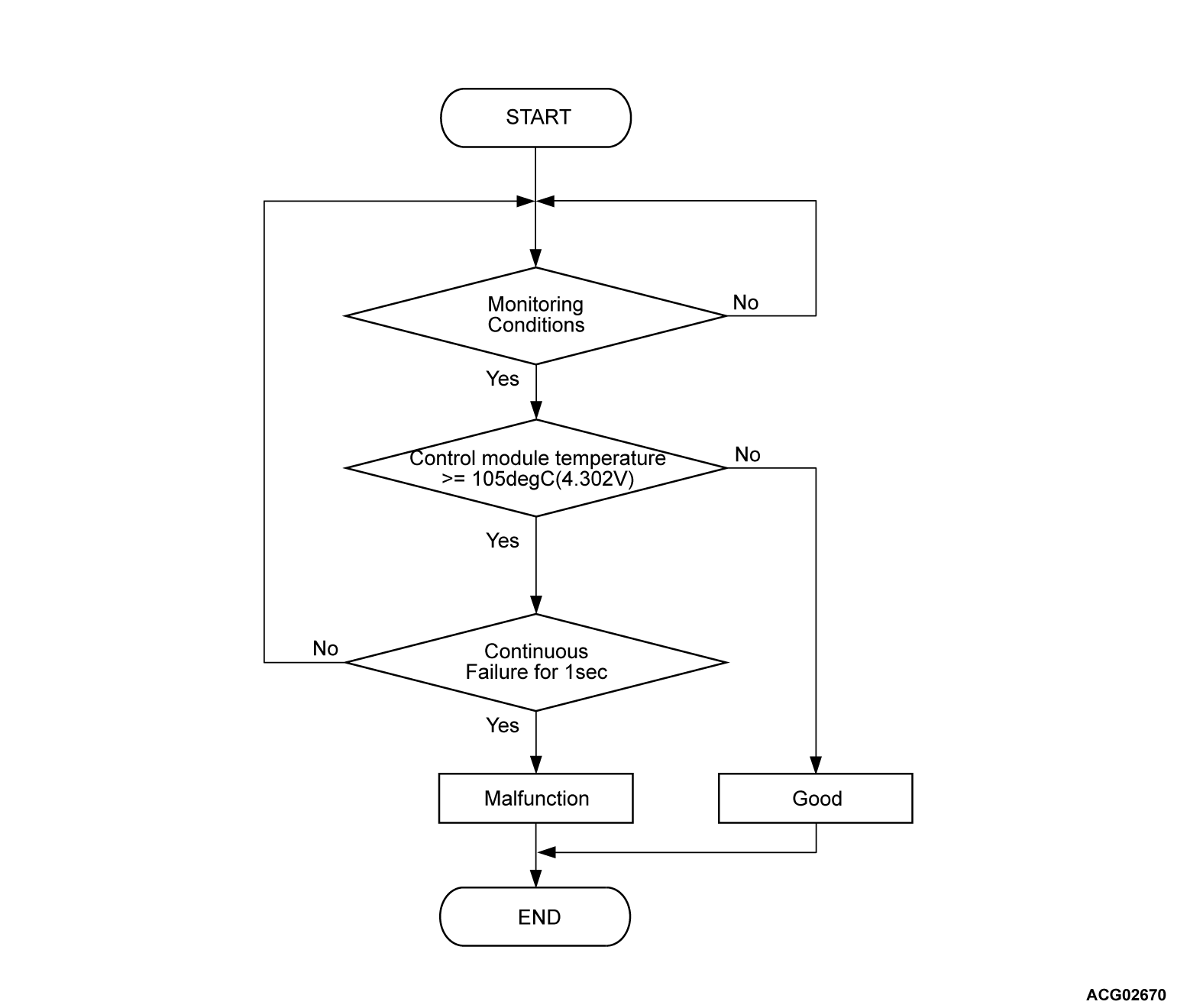
Check Conditions <DTC P1015>
- Power drive unit (GCU) power supply voltage is 8 volts to 16 volts.
Judgment Criterion <DTC P1015>
- Change of the power drive unit (GCU) module temperature sensor temperature is more than 105°C (221°F) (4.302 volts) for 1 second.
PROBABLE CAUSES
- The EV cooling system fails (radiator fan, electric water pump, coolant)
- Pipe clogging
- Harness abnormality
- Electric oil pump relay abnormality
- Malfunction of the power drive unit [generator control unit (GCU)]
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check whether the other DTC is set.
Check whether the PHEV-ECU set a DTC P0A05 or P10D9 which is related to the electric water pump.
Is the DTC set?
STEP 2. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check whether the other DTC is set.
Check whether the PHEV-ECU set a DTC P0691, P0692, P0693, P0694, P10DE or P10DF which is related to the fan, fan motor and fan shroud assembly.
Is the DTC set?
STEP 3. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check the actuator test.
Check the following actuator test (Refer to GROUP 54Da - PHEV-ECU - Actuator Test Reference Table  ).
).
 ).
).- Item No.3: Radiator fan relay 1 actuate
- Item No.4: Radiator fan relay 2 actuate
Is the check result normal?
STEP 4. Check the EV radiator.
Visually check that the fins of the EV radiator are not dented or deformed.
Is the check result normal?
STEP 5. Check the motor coolant level.
Check that the motor coolant level is normal. (Refer to GROUP 14B - Motor Coolant Check  ).
).
 ).
).Is the check result normal?
STEP 6. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check the special function.
(1) Execute the following special function (Refer to GROUP 54Da - PHEV-ECU - Special Function, Test  ).
).
 ).
).- Item 2: Water pump actuate
(2) When forcibly driving the electric water pump, check that the coolant in the EV radiator condenser tank is flowing.
Is coolant flowing?
 Replace the water hose and water pipe (Refer to GROUP 14B - Water Hose and Water Pipe
Replace the water hose and water pipe (Refer to GROUP 14B - Water Hose and Water Pipe  <Front>,
<Front>,  <Center>,
<Center>,  <Rear>), the electric water pump (Refer to GROUP 14B - Water Pump
<Rear>), the electric water pump (Refer to GROUP 14B - Water Pump  ), the power drive unit (Refer to
), the power drive unit (Refer to  ), the REMCU (Refer to
), the REMCU (Refer to  ), the rear motor assembly (Refer to
), the rear motor assembly (Refer to  ) and the on board charger/DC-DC converter (Refer to GROUP 54Dd - On Board Charger (OBC) /DC-DC Converter
) and the on board charger/DC-DC converter (Refer to GROUP 54Dd - On Board Charger (OBC) /DC-DC Converter  ). Then go to Step 7
). Then go to Step 7 .
.STEP 7. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check the special function.
(1) Execute the following special function (Refer to GROUP 54Da - PHEV-ECU - Special Function, Test  ).
).
 ).
).- Item 2: Water pump actuate
(2) When forcibly driving the electric water pump, check that the coolant in the EV radiator condenser tank is flowing.
Is coolant flowing?
 Replace the water hose and water pipe (Refer to GROUP 14B - Water Hose and Water Pipe
Replace the water hose and water pipe (Refer to GROUP 14B - Water Hose and Water Pipe  <Front>,
<Front>,  <Center>,
<Center>,  <Rear>), the electric water pump (Refer to GROUP 14B - Water Pump
<Rear>), the electric water pump (Refer to GROUP 14B - Water Pump  ), the power drive unit (Refer to
), the power drive unit (Refer to  ), the REMCU (Refer to
), the REMCU (Refer to  ), the rear motor assembly (Refer to
), the rear motor assembly (Refer to  ) and the on board charger/DC-DC converter (Refer to GROUP 54Dd - On Board Charger (OBC) /DC-DC Converter
) and the on board charger/DC-DC converter (Refer to GROUP 54Dd - On Board Charger (OBC) /DC-DC Converter  ). Then go to Step 6
). Then go to Step 6 .
.![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)