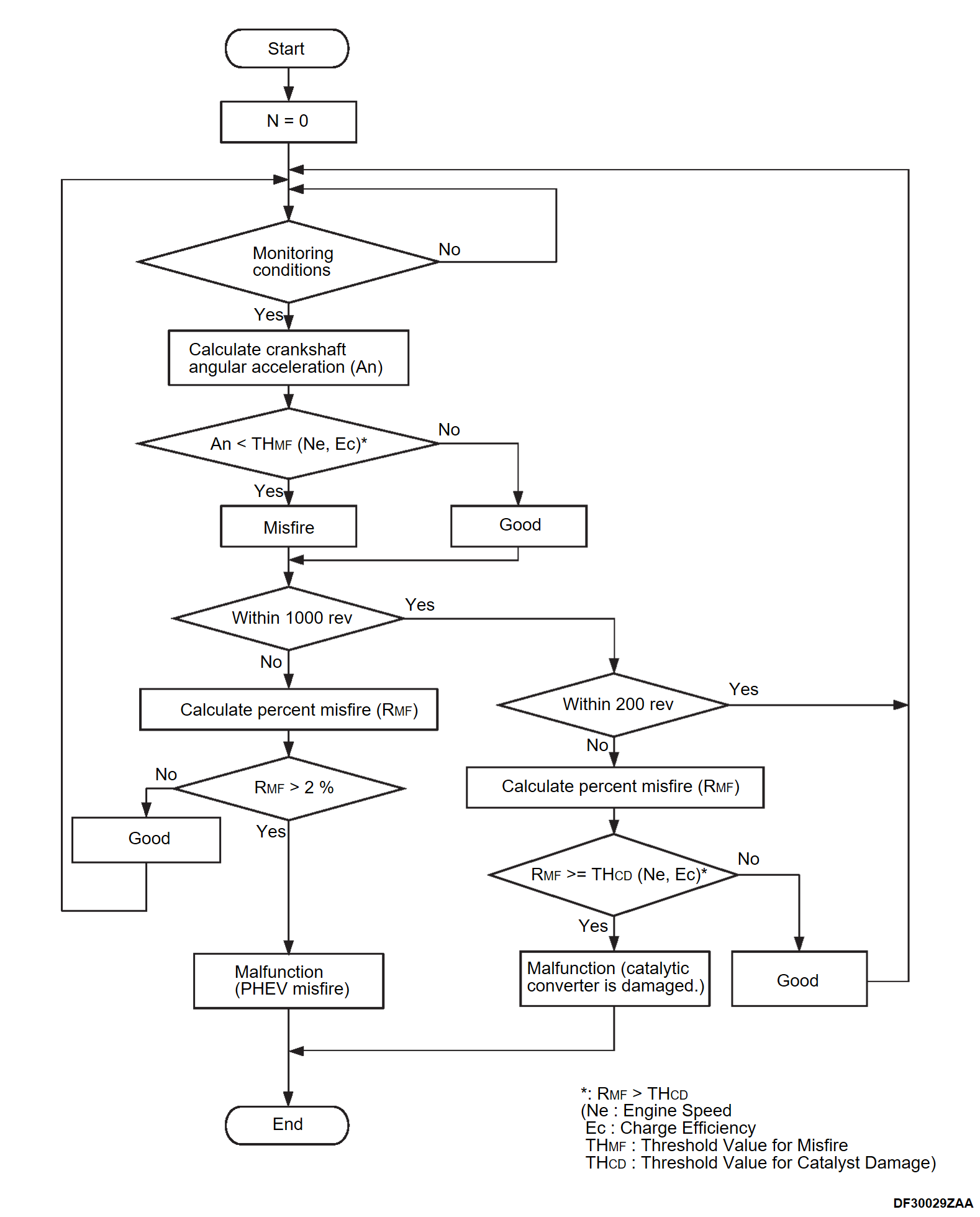
DTC P0300-00: Misfire monitor(Random/multiple cylinder misfire detected)
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
- If a misfire occurs while the engine is running, the engine speed changes for an instant.
- The ECM checks for such changes in engine speed.
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
Monitor angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect malfunction when negative variation of the angular acceleration is large.
MONITOR EXECUTION
Continuous.
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC set in memory for the item monitored below)
- Not applicable
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Camshaft position sensor
- Mass airflow sensor
- Engine coolant temperature sensor
- Intake air temperature sensor
- Barometric pressure sensor
- Throttle position sensor
- Fuel tank pressure sensor
DTC SET CONDITIONS
Check Conditions
- Engine speed is between 188 and 5,250 r/min.
- The engine load is with in the positive torque load.
- Barometric pressure is higher than 76 kPa (22.4 in.Hg).
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than –10°C (14°F).or
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than 20°C (68°F) <When engine coolant temperature is –10°C (14°F) or lower at engine start>
- Adaptive learning is complete for the vane which generates a crankshaft position signal.
- While the engine is running, excluding sudden acceleration/deceleration and fuel shut-off operation.
Judgment Criterion (change in the angular acceleration of the crankshaft is used for misfire detection)
- Misfire counts per 1,000 revolutions exceeds in 2.0 percent.
Check Conditions
- Engine speed is between 188 and 5,250 r/min.
- The engine load is with in the positive torque load.
- Barometric pressure is higher than 76 kPa (22.4 in.Hg).
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than –10°C (14°F).or
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than 20°C (68°F) <When engine coolant temperature is –10°C (14°F) or lower at engine start>
- Adaptive learning is complete for the vane which generates a crankshaft position signal.
- While the engine is running, excluding sudden acceleration/deceleration and fuel shut-off operation.
Judgment Criterion (change in the angular acceleration of the crankshaft is used for misfire detection)
- Misfire has occurred more frequently than allowed during the last 200 revolutions [when the catalyst temperature is higher than 1,000°C (1,832°F)].
FAIL-SAFE AND BACKUP FUNCTION
The supply of fuel to the misfiring cylinder can possibly be cut.
OBD-II DRIVE CYCLE PATTERN
Refer to Diagnostic Function, OBD-II Drive Cycle – Pattern 2 OBD- II DRIVE CYCLE .
.
 .
.TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS (The most likely causes for this code to be set are:)
- Included air due to lack of fuel
- Ignition system related part(s) failed.
- Crankshaft position sensor failed.
- Fuel injector failed.
- Incorrect air-fuel ratio.
- Low compression pressure.
- Intake air temperature sensor (built into the mass airflow sensor) failed.
- Engine coolant temperature sensor failed.
- Mass airflow sensor failed.
- Skipping of timing chain teeth.
- EGR system and EGR valve failed.
- EGR valve stuck (jamming of foreign materials).
- Peak torque limiter failed.
- ECM failed.
DIAGNOSIS
Required Special Tools:
- MB992744: Vehicle communication interface-Lite (V.C.I.-Lite)
- MB992745: V.C.I.-Lite main harness A
- MB992747: V.C.I.-Lite USB cable short
- MB992748: V.C.I.-Lite USB cable long
1.STEP 1. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-III SE), check the data list.
Use scan tool (M.U.T.-III SE) to check the data list (Refer to DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE ).
). Perform the DTC classified check procedure for the sensor that has shown an abnormal data value (Refer to DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
Perform the DTC classified check procedure for the sensor that has shown an abnormal data value (Refer to DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART ).
).
 ).
).- Item number 40: Crank Angle Sensor (Engine RPM)
- Item number 50: Air Temperature Sensor
- Item number 60: Coolant (Water) Temperature Sensor
- Item number 80: Air flow Sensor
- Item number 140: Short term fuel trimming (bank1)
- Item number 150: Long term fuel trimming (bank1)
Q: Are the check result normal?
 Perform the DTC classified check procedure for the sensor that has shown an abnormal data value (Refer to DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
Perform the DTC classified check procedure for the sensor that has shown an abnormal data value (Refer to DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART ).
).2.STEP 2. Visual check of ignition spark.
(1) Remove the spark plug and attach the removed spark plug to the ignition coil (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Electrical – Ignition Coil IGNITION COIL REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
).
 ).
).(2) Disconnect the fuel injector connectors for all cylinders.
(3) Connect the ignition coil connector.
(4) Ground the ground electrode of the spark plug, and set the vehicle to the continuous idling mode (Refer to GENERAL INFORMATION, General Information – Precautions CONTINUOUS IDLING MODE ).
).
 ).
).(5) Check that the electrode of the spark plug sparks.
Q: Is the check result normal?
 Perform troubleshooting for the ignition system (Refer to Symptom Procedure for Inspection procedure 13: Ignition Circuit System Ignition circuit system
Perform troubleshooting for the ignition system (Refer to Symptom Procedure for Inspection procedure 13: Ignition Circuit System Ignition circuit system ).
).3.STEP 3. Check fuel injector itself.
Check number 1 cylinder fuel injector, number 2 cylinder fuel injector, number 3 cylinder fuel injector and number 4 cylinder fuel injector itself (Refer to FUEL INJECTOR CHECK ).
). Replace the fuel injector (Refer to FUEL INJECTOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Replace the fuel injector (Refer to FUEL INJECTOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
).
 ).
).Q: Are the check result normal?
 Replace the fuel injector (Refer to FUEL INJECTOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Replace the fuel injector (Refer to FUEL INJECTOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
).4.STEP 4. Check air intake from air cleaner throttle body duct and intake manifold.
5.STEP 5. Fuel pressure measurement.
6.STEP 6. Check the timing mark on the timing chain.
Check that the timing mark of the timing chain is correct (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Mechanical – Camshaft CAMSHAFT REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
). Align the timing mark on the timing chain (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Overhaul – Timing Chain TIMING CHAIN REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Align the timing mark on the timing chain (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Overhaul – Timing Chain TIMING CHAIN REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
).
 ).
).Q: Is the check result normal?
 Align the timing mark on the timing chain (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Overhaul – Timing Chain TIMING CHAIN REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Align the timing mark on the timing chain (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Overhaul – Timing Chain TIMING CHAIN REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
).7.STEP 7. Check compression pressure.
Check the compression pressure (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Mechanical – On-vehicle Service COMPRESSION PRESSURE CHECK ).
). Repair it.
Repair it.
 ).
).Q: Is the check result normal?
 Repair it.
Repair it.8.STEP 8. Check fuel.
Check for entry of foreign matter (water, diesel fuel, etc.) into fuel. Replace the fuel.
Replace the fuel.
Q: Is the check result normal?
 Replace the fuel.
Replace the fuel.9.STEP 9. Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve fully closed state check.
(1) Use scan tool (M.U.T.-III SE) to check the PHEV-ECU data list item number 110: SOC for display (Refer to ELECTRIC POWER TRAI N, PHEV-ECU - Troubleshooting - Data List Reference Table DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE ). If the drive battery has a charge of less than 30 percent, charge it to at least 30 percent.
). If the drive battery has a charge of less than 30 percent, charge it to at least 30 percent.
 ). If the drive battery has a charge of less than 30 percent, charge it to at least 30 percent.
). If the drive battery has a charge of less than 30 percent, charge it to at least 30 percent.(2) Set the vehicle to the continuous idling mode (Refer to GENERAL INFORMATION, General Information – Precautions CONTINUOUS IDLING MODE ).
).
 ).
).(3) Use scan tool (M.U.T.-III SE) to check the data list (Refer to DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE ).
).
 ).
).- Item number 70: Boost Sensor
OK: 28.3 to 41.7 kPa (8.4 to 12.3 in.Hg)
| note | If the EGR valve does not close fully due to jamming of foreign materials, the exhaust gas flows in the intake manifold and the pressure value rises. |
Q: Is the check result normal?
 Replace the EGR valve [Refer to ENGINE, Engine, Motor and Emission Control – Emission Control – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) VALVE REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Replace the EGR valve [Refer to ENGINE, Engine, Motor and Emission Control – Emission Control – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) VALVE REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ].
].10.STEP 10. Peak torque limiter deterioration check.
(1) Set the vehicle to the continuous idling mode (Refer to GENERAL INFORMATION, General Information – Precautions CONTINUOUS IDLING MODE ).
).
 ).
).(2) Press the accelerator pedal and maintain an engine speed of 1,700 to 1,900 r/min. For the engine speed, use scan tool (M.U.T.-III SE) to select and check the data list item number 40: Crank Angle Sensor (Engine RPM) (Refer to DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE ).
).
 ).
).| note | When the charge state is 30 to 60 percent, the engine speed follows the accelerator pedal operation. The charge state can be checked in PHEV-ECU data list item number 110: SOC for display (Refer to ELECTRIC POWER TRAI N, PHEV-ECU – Troubleshooting – Data List Reference Table DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE ). ). |
Q: Is noise (drive system-related rattle sound) heard?
 Replace the peak torque limiter (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Overhaul – Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Replace the peak torque limiter (Refer to ENGINE, Engine Overhaul – Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
).11.STEP 11. Test the OBD-II drive cycle.
After erasing the DTC, carry out test drive with the drive cycle pattern, and recheck the DTC. Replace the ECM (Refer to ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Replace the ECM (Refer to ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
). Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GENERAL INFORMATION, General Information – How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection Service Points – How to Cope with Intermittent Malfunctions HOW TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT MALFUNCTIONS
Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GENERAL INFORMATION, General Information – How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection Service Points – How to Cope with Intermittent Malfunctions HOW TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT MALFUNCTIONS ).
).
(1) Use scan tool (M.U.T.-III SE) to erase the DTC.
(2) Carry out test drive with the drive cycle pattern (Refer to Diagnostic Function, OBD-II Drive Cycle – Pattern 2 OBD- II DRIVE CYCLE ).
).
 ).
).(3) Use scan tool (M.U.T.-III SE) to recheck the DTC.
Q: Is DTC P0300-00 set?
 Replace the ECM (Refer to ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Replace the ECM (Refer to ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ).
). Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GENERAL INFORMATION, General Information – How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection Service Points – How to Cope with Intermittent Malfunctions HOW TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT MALFUNCTIONS
Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GENERAL INFORMATION, General Information – How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection Service Points – How to Cope with Intermittent Malfunctions HOW TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT MALFUNCTIONS ).
).![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)