DTC B1400: Driver's air bag module (1st squib) system (short circuit between squib circuit terminals)
DTC B1480: Driver's air bag module (2nd squib) system (short circuit between squib circuit terminals)
DTC B1480: Driver's air bag module (2nd squib) system (short circuit between squib circuit terminals)
| caution |
|
CIRCUIT OPERATION
- The SRS-ECU judges how severe a collision is by detecting signals from the front impact sensors and the G-sensor in the SRS-ECU. If the impact is over a predetermined level, the SRS-ECU sends an ignition signal. At this time, the SRS air bag will inflate.
- The ignition signal is input to the air bag module via the clock spring to inflate the air bag.
DTC SET CONDITIONS
- This DTC is stored if there is abnormal resistance between the input terminals of the driver's air bag module (squib). The most likely causes for this code to be stored are the followings:
- Short circuit in driver’s air bag module (squib) or harness
- Short circuit in the clock spring
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
- Improper engaged connector or defective short spring*
- Short circuit in the clock spring
- Short circuit between the driver's air bag module (squib) circuit terminals
- Damaged connector(s)
- Malfunction of the SRS-ECU
| note | *: The squib circuit connectors integrate a "short" spring (which prevents the air bag from deploying unintentionally due to static electricity by shorting the positive wire to the ground wire in the squib circuit when the connectors are disconnected). Therefore, if connector is damaged or improperly engaged, the short spring may not be released when the connector is connected. |
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-III), diagnose the CAN bus line.
| caution | To prevent damage to scan tool (M.U.T.-III), always turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position before connecting or disconnecting scan tool (M.U.T.-III). |
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(3) Diagnose the CAN bus line.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the CAN bus line found to be normal?
STEP 2. Recheck for diagnostic trouble code.
Check again if the DTC is stored.
(1) Erase the DTC.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to "ON" position.
(3) Check if the DTC is stored.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the DTC stored?
STEP 3. Connector check: SRS-ECU, clock spring, driver's air bag module.
(1) Check that the negative battery terminal is disconnected. If the negative battery terminal is connected, disconnect it.
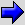
(2) While pushing the part "A" indicated in the figure of the harness side connector, turn the lock lever to the direction of the arrow to release the lock lever. After disconnecting the SRS-ECU connector, connect it again.
(3) After disconnecting clock spring, connect it again.
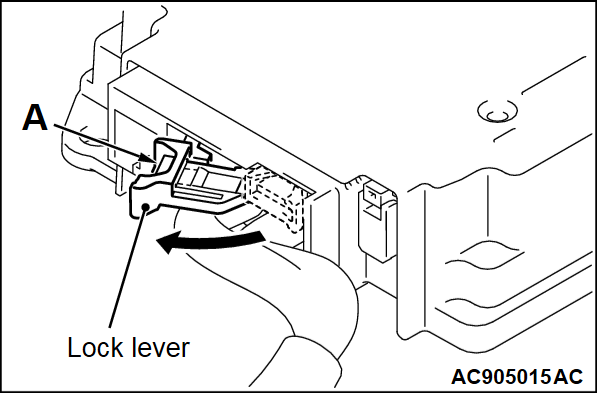
(4) Disconnect the driver's air bag module connector using the slotted (-) screwdriver to pull out the locking button to the direction of the arrow, and connect it again.
(5) Connect the negative battery terminal.
(6) After erasing the diagnostic trouble code memory, check the diagnostic trouble code again.
(7) Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
Is DTC B1400 <1st squib> or B1480 <2nd squib> stored?
 Replace the connector concerned.
Replace the connector concerned.STEP 4. Diagnosis check by dummy resistor connection.
(1) Check that the negative battery terminal is disconnected. If the negative battery terminal is connected, disconnect it.
(2) Use the flat-tipped screwdriver to pull out the locking button of wiring harness side connector, and release the lock.
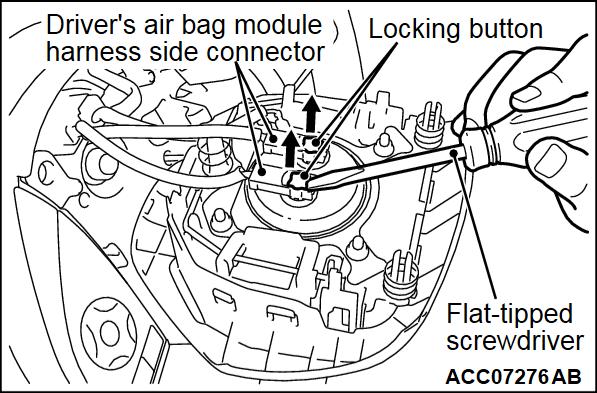
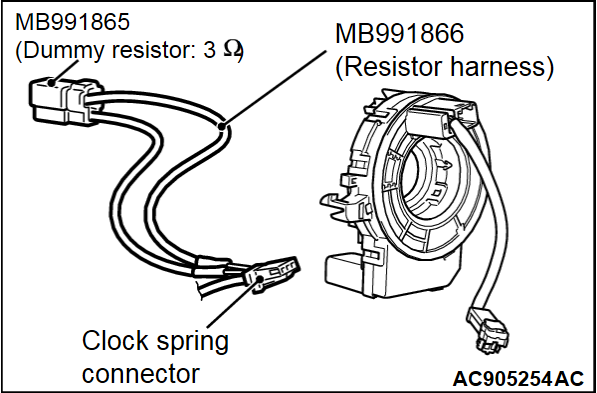
(3) Connect special tool dummy resistor (MB991865) to special tool resistor harness (MB991866).
(4)
Insert the resistor harness probe (special tool) as shown.
| caution | Do not insert a probe directly into the terminal from the connector front side as the connector contact pressure may be weakened. |
(5) Connect the negative battery terminal.
(6) After erasing the diagnostic trouble code memory, check the diagnostic trouble code again.
(7) Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
(8)
| caution | Always DTC B1480 is stored when checking DTC B1400. This is because the second side terminal is isolated when checking it. DTC B1480 is stored but this is not a fault. In addition, always DTC B1400 is stored when checking DTC B1480 because the first side terminal is isolated. |
Erase the diagnostic trouble code memory, and check the diagnostic trouble code.
Is DTC B1400 <1st squib> or B1480 <2nd squib> stored?
STEP 5. Diagnosis check by dummy resistor connection.
(1) Check that the negative battery terminal is disconnected. If the negative battery terminal is connected, disconnect it.
(2) Disconnect the clock spring connector.
(3) Connect special tool dummy resistor (MB991865) to special tool resistor harness (MB991866).
(4)
| caution | Do not insert a probe directly into the terminal from the connector front side as the connector contact pressure may be weakened. |
Insert the resistor harness probe from the back of harness side connector DQ1-, DQ1+ line <B1400>.
Insert the resistor harness probe from the back of harness side connector DQ2-, DQ2+ line <B1480>.
(5) Connect the negative battery terminal.
(6) After erasing the diagnostic trouble code memory, check the diagnostic trouble code again.
(7) Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
(8)
| caution | Always DTC B1480 is stored when checking DTC B1400. This is because the second side terminal is isolated when checking it. DTC B1480 is stored but this is not a fault. In addition, always DTC B1400 is stored when checking DTC B1480 because the first side terminal is isolated. |
Erase the diagnostic trouble code memory, and check the diagnostic trouble code.
Is DTC B1400 <1st squib> or B1480 <2nd squib> stored?
STEP 6. Resistance measurement at the SRS-ECU connector.
(1) Check that the negative battery terminal is disconnected. If the negative battery terminal is connected, disconnect it.
(2) While pushing the part "A" indicated in the figure of the harness side connector, turn the lock lever to the direction of the arrow to release the lock lever, and disconnect the SRS-ECU connector.
(3)
| caution | To release SRS-ECU connector short spring in the following operations, disconnect this clock spring connector, and keep the squib circuit shorted. |
Disconnect the clock spring connector.
(4)
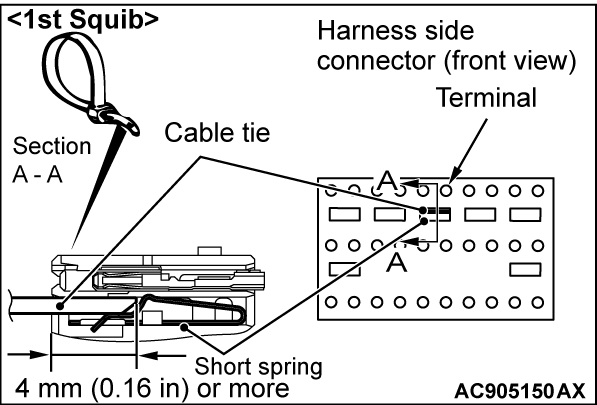
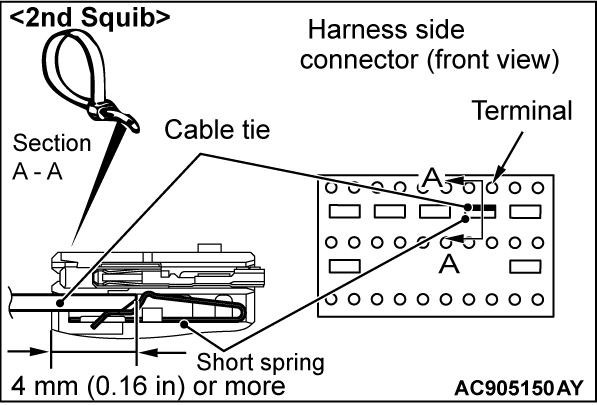
| caution | The short spring may not be released due to the insufficient insertion. Therefore, insert the insulator for 4 mm (0.16 inch) or more. |
Insert the insulator [width: 3 mm (0.12 inch), thickness: 0.5 mm (0.02 inch)] such as cable tie between the DQ1-, DQ1+ line, and then release the short spring <B1400>.
Insert the insulator [width: 3 mm (0.12 inch), thickness: 0.5 mm (0.02 inch)] such as cable tie between the DQ2-, DQ2+ line, and then release the short spring <B1480>.
(5) Take the measurements below at the harness side connector.
- Continuity between DQ1-, DQ1+ line <B1400>
OK: No continuity
- Continuity between DQ2-, DQ2+ line <B1480>
OK: No continuity
Is the check result normal?
 Repair the wiring harnesses DQ1-, DQ1+ line <B1400> or DQ1-, DQ1+ line <B1480> between the clock spring connector and the SRS-ECU connector.
Repair the wiring harnesses DQ1-, DQ1+ line <B1400> or DQ1-, DQ1+ line <B1480> between the clock spring connector and the SRS-ECU connector. STEP 7. Recheck for diagnostic trouble code.
Check again if the DTC is stored.
(1) Erase the DTC.
(2) Turn the electric motor switch to the "ON" position.
(3) Check if the DTC is stored.
(4) Turn the electric motor switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is DTC B1400 <1st squib> or B1480 <2nd squib> stored?
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)