DTC P0172: System too Rich
Fuel Trim Circuit
CIRCUIT OPERATION
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
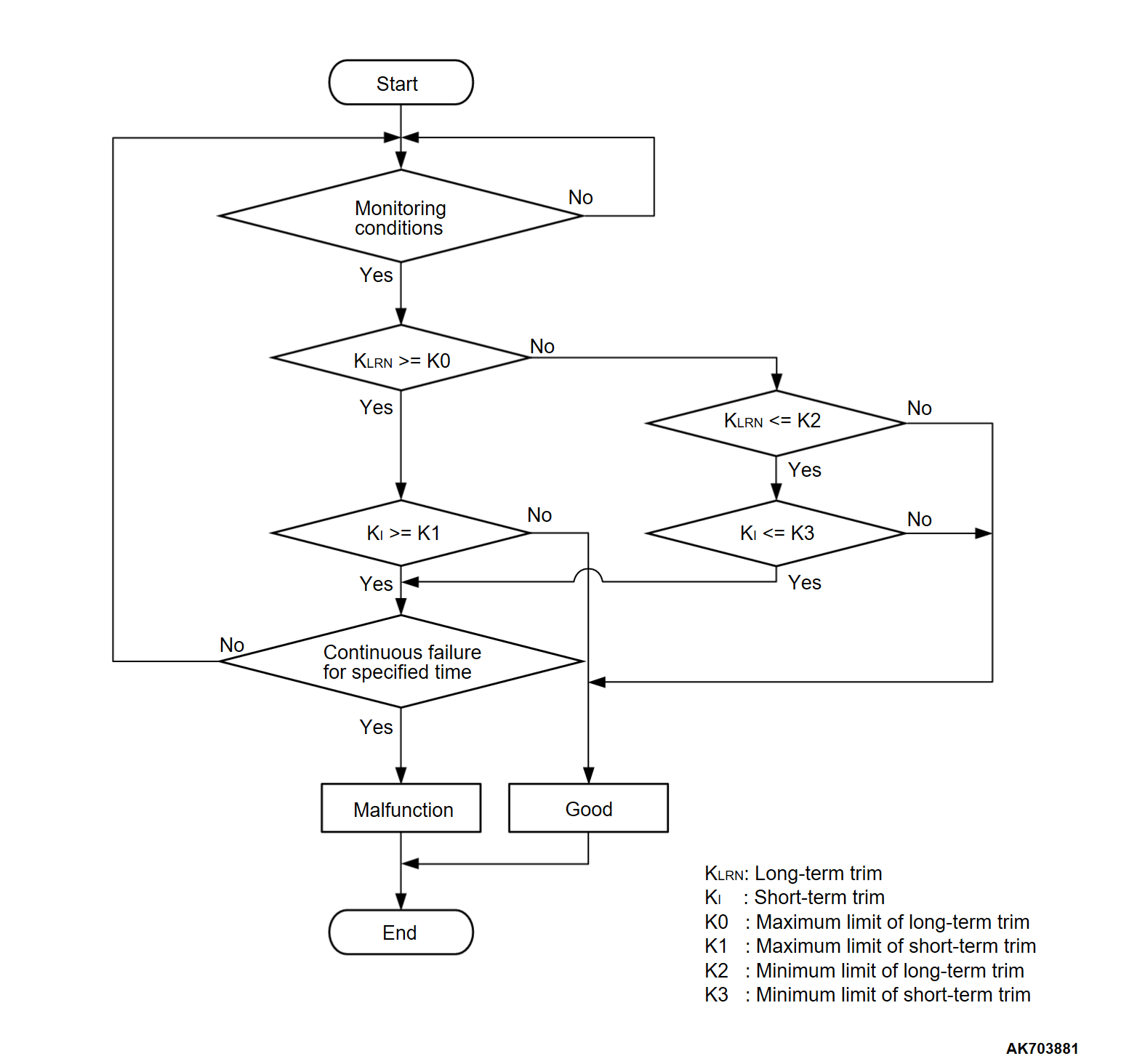
- If a malfunction occurs in the fuel system, the fuel trim value becomes too large.
- The ECM checks whether the fuel trim value is within a specified range.
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
- Air/fuel learning value (long time fuel trim) and air/fuel feedback integral value (short time fuel trim) are too lean.
MONITOR EXECUTION
- Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC set in memory for the item monitored below)
- Misfire monitor
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Mass airflow sensor
- Engine coolant temperature sensor
- Intake air temperature sensor 1
- Intake air temperature sensor 2
- Barometric pressure sensor
- Throttle position sensor
- Manifold absolute pressure sensor
- Boost pressure sensor
Check Conditions
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than 76°C (169°F).
- Under the closed loop air/fuel ratio control.
- Monitor disabled stroke is 0 condition.
- Mass airflow sensor output is 7.68 g/sec or more.
- Fuel injection mode is MFI-mode.
Judgment Criterion
- Long-term fuel trim has continued to be higher than -12.5 percent for 5 seconds.
- Short-term fuel trim has continued to be higher than -7.8 percent for 5 seconds.
Check Conditions
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than 76°C (169°F).
- Under the closed loop air/fuel ratio control.
- Monitor disabled stroke is 0 condition.
- Mass airflow sensor output is 7.68 g/sec or less.
- Fuel injection mode is MFI-mode.
Judgment Criterion
- Long-term fuel trim has continued to be higher than -12.5 percent for 5 seconds.
- Short-term fuel trim has continued to be higher than -12.9 percent for 5 seconds.
Check Conditions
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than 76°C (169°F).
- Under the closed loop air/fuel ratio control.
- Monitor disabled stroke is 0 condition.
- Mass airflow sensor output is 7.68 g/sec or more.
- Fuel injection mode is not MFI-mode.
Judgment Criterion
- Long-term fuel trim has continued to be higher than -12.5 percent for 5 seconds.
- Short-term fuel trim has continued to be higher than -5.5 percent for 5 seconds.
Check Conditions
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than 76°C (169°F).
- Under the closed loop air/fuel ratio control.
- Monitor disabled stroke is 0 condition.
- Fuel injection mode is MFI-mode.
Judgment Criterion
- Long-term fuel trim has continued to be -12.5 percent for 2 seconds.
- Short-term fuel trim has continued to be -25.0 percent for 2 seconds.
Check Conditions
- Engine coolant temperature is higher than 76°C (169°F).
- Under the closed loop air/fuel ratio control.
- Monitor disabled stroke is 0 condition.
- Fuel injection mode is not MFI-mode.
Judgment Criterion
- Long-term fuel trim has continued to be -12.5 percent for 2 seconds.
- Short-term fuel trim has continued to be -25.0 percent for 2 seconds.
FAIL-SAFE AND BACKUP FUNCTION
- None.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS (The most likely causes for this code to be set are: )
- Mass airflow sensor failed.
- Injector failed.
- Incorrect fuel pressure.
- Contamination around the throttle valve
- Engine coolant temperature sensor failed.
- Intake air temperature sensor 1 failed.
- Intake air temperature sensor 2 failed.
- Barometric pressure sensor in the ECM failed.
- Manifold absolute pressure sensor failed.
- Exhaust leak.
- Use of incorrect or contaminated fuel.
- Fuel system related part(s) circuit harness damage, or connector damage.
- Boost pressure sensor failed.
- Air intake from mass airflow sensor and all components downstream of it.
- Linear air-fuel sensor failed.
- Evaporative emission control system failed.
- Positive crankcase ventilation valve failed.
- Injector (high pressure) failed.
- ECM failed.
DIAGNOSIS
Preparation to carry out troubleshooting
- Store the freeze frame data of the DTC P0172.
STEP 1. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), read the diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
| caution | To prevent damage to scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), always turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position before connecting or disconnecting scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE). |
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(3) Read the DTC.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the diagnostic trouble code other than P0172 set?
STEP 2. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 5: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 5, Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1.
- The intake air temperature and temperature shown with the scan tool should approximately match.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 3. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 6: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 6, Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor.
- The engine coolant temperature and temperature shown with the scan tool should approximately match.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 4. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 8: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 8, Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor.
- When altitude is 0 m (0 foot), 101 kPa (29.8 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 600 m (1,969 feet), 95 kPa (28.1 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 1,200 m (3,937 feet), 88 kPa (26.0 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 1,800 m (5,906 feet), 81 kPa (23.9 in.Hg).
(3) Start the engine.
- When the engine is idling, 70 - 110 kPa (20.7 - 32.4 in.Hg) (Near the atmospheric pressure).
- When the engine is suddenly revved, manifold absolute pressure varies.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 5. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 10: Mass Airflow Sensor.
(1) Start the engine and run at idle.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 10, Mass Airflow Sensor.
(3) Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature: 80°C to 95°C (176°F to 203°F).
- The standard value during idling should be between 800 and 1,120 millivolts.
- When the engine is revved, the mass airflow rate should increase according to the increase in engine speed.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 6. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item BB: Barometric Pressure Sensor.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item BB, Barometric Pressure Sensor.
- When altitude is 0 m (0 foot), 101 kPa (29.8 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 600 m (1,969 feet), 95 kPa (28.1 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 1,200 m (3,937 feet), 88 kPa (26.0 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 1,800 m (5,906 feet), 81 kPa (23.9 in.Hg).
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 7. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item DE: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 2.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item DE, Intake Air Temperature Sensor 2.
- The intake air temperature and temperature shown with the scan tool should approximately match.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 8. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 125: Boost Pressure Sensor.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 125, Boost Pressure Sensor.
- When altitude is 0 m (0 foot), 101 kPa (29.8 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 600 m (1,969 feet), 95 kPa (28.1 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 1,200 m (3,937 feet), 88 kPa (26.0 in.Hg).
- When altitude is 1,800 m (5,906 feet), 81 kPa (23.9 in.Hg).
(3) Start the engine.
- When the engine is idling, 70 - 110 kPa (20.7 - 32.4 in.Hg) (Near the atmospheric pressure).
- When the engine is suddenly revved, intake charge pressure varies.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 9. Check the positive crankcase ventilation system.
Refer to GROUP 17, Emission Control - Positive Crankcase Ventilation System - Positive Crankcase Ventilation System Check  .
.
 .
.Is the positive crankcase ventilation system normal?
STEP 10. Check the throttle body. (throttle valve area)
Is the throttle valve area dirty?
STEP 11. Check air intake from mass airflow sensor mounting position and all components downstream of it.
STEP 12. Check for exhaust leak.
STEP 13. Check installation status of linear air-fuel sensor.
STEP 14. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item E1: Linear Air-Fuel Ratio Sensor.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item E1, Linear Air-Fuel Ratio Sensor.
(3) Warm up the engine.
- When the engine is running at 4,000 r/min is 2.0 volts or less → 3.5 volts or more (After several seconds have elapsed).
- When the engine is suddenly revved is 2.0 volts or less.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 15. Check the evaporative emission purge solenoid.
Refer to GROUP 17, Emission Control - Evaporative Emission Control System - Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid Check  .
.
 .
.Is the evaporative emission purge solenoid normal?
STEP 16. Check of harness damage in PURG line between evaporative emission purge solenoid connector and ECM connector.
Is the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 17. Check of harness damage in power supply line between MFI relay connector and evaporative emission purge solenoid connector.
Is the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 18. Check the vacuum hose.
STEP 19. Check evaporative emission control system.
Refer to GROUP 17, Emission Control - Evaporative Emission Control System - Purge Control System Check (purge flow check)  .
.
 .
.Is the evaporative emission control system normal?
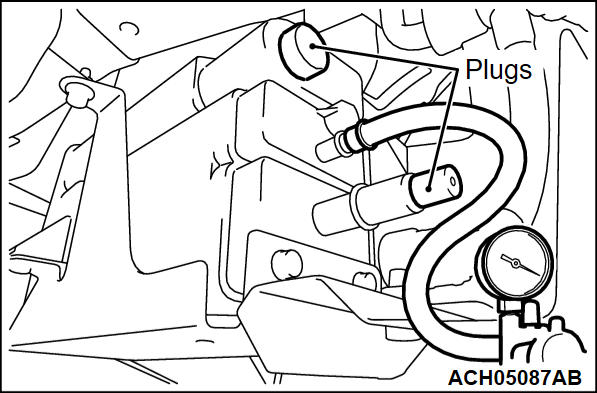
STEP 20. Check the evaporative emission canister.
(1) Visually check for cracks or other leaks in the evaporative emission canister.
(2) Connect a hand vacuum pump to the evaporative emission canister and plug the other nipples.
(3) Apply a pressure on the hand vacuum pump, and confirm that air is maintained.
(4) Disconnect the hand vacuum pump and remove the plugs.
Is the evaporative emission canister in good condition?
STEP 21. Check the evaporative emission ventilation solenoid.
Refer to GROUP 17, Emission Control - Evaporative Emission Canister and Fuel Tank Pressure Relief Valve - Inspection  .
.
 .
.Is the evaporative emission ventilation solenoid normal?
STEP 23. Check of harness damage in INJ1, INJ2, INJ3, INJ4 line between injector connectors and ECM connector.
Are the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 24. Check of harness damage in power supply line between MFI relay connector and injector connectors.
Are the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 25. Check the injector (high pressure).
STEP 26. Check of harness damage in DI-1, DI-2, DI-3, DI-4 line between injector (high pressure) connectors and ECM connector.
Are the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 27. Check of harness damage in DI+1, DI+2, DI+3, DI+4 line between injector (high pressure) connectors and ECM connector.
Are the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 29. Check for entry of foreign matter (water, diesel fuel, etc.) into fuel.
STEP 30. After checking stored freeze frame data, check DTC again.
- If DTC P0172 is set while the vehicle is idling, let the vehicle idle for more than 20 minutes.
- If DTC P0172 is set while the vehicle is running, let the vehicle run with the same conditions of the freeze frame data, such as the vehicle speed, the crank angle sensor and the coolant temperature sensor, for more than 10 minutes.
Is DTC P0172 set?
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)