DTC P0400: Exhaust Gas Recirculation System
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
- When the EGR valve (stepper motor) is actuated from the fully closed position toward the open position while the engine is running, EGR gas flows.
- The ECM checks how the EGR gas flow signal changes.
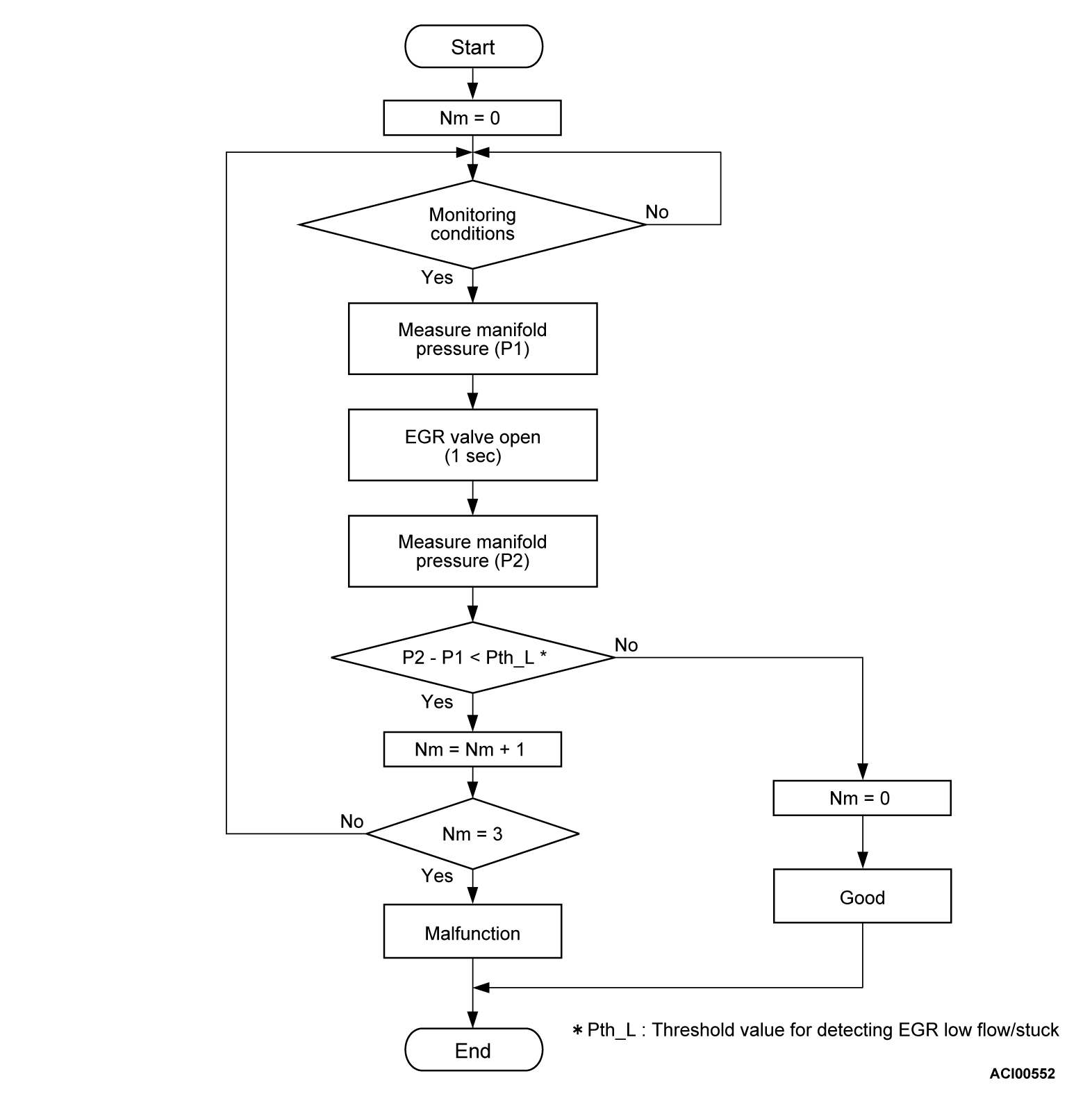
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
- Small manifold pressure change during exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) operation from closed to open.
MONITOR EXECUTION
- Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC set in memory for the item monitored below)
- Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) stepper motor monitor
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Mass airflow sensor
- Engine coolant temperature sensor
- Intake air temperature sensor
- Barometric pressure sensor
- Accelerator pedal position sensor
- Manifold absolute pressure sensor
Check Conditions
- At least 20 seconds have passed since the last monitor was complete.
- Engine coolant temperature is more than 76°C (169°F).
- Engine speed is between 1,188 and 2,500 r/min.
- Intake air temperature is more than -10°C (14°F).
- Barometric pressure is more than 76 kPa (22.4 in.Hg).
- Fuel is being shut off.
- Vehicle speed is more than 30 km/h (19 mph).
- At least 90 seconds have passed since manifold absolute pressure sensor output voltage fluctuated more than 1.5 volts.
- Battery positive voltage is more than 10.3 volts.
- Accelerator pedal is not depressed.
- Volumetric efficiency is less than 24 percent.
- The ECM monitors for this condition for 3 cycles of 1.8 seconds each during the drive cycle.
Judgment Criterion
- When the EGR valve opens to the prescribed opening, the intake manifold pressure fluctuation width is less than 2.5 kPa (0.74 in.Hg).
FAIL-SAFE AND BACKUP FUNCTION
- None
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS (The most likely causes for this code to be set are:)
- Contaminated EGR valve and EGR passage.
- ECM failed.
DIAGNOSIS
Required Special Tool:
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: V.C.I.
- MB991827: USB Cable
- MB991910: Main Harness A
STEP 1. Check the EGR system
Refer to GROUP 17, Emission Control - Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System - General Information  .
.
 .
.Are there any abnormalities?
STEP 2. Check the EGR valve contamination and the EGR passage contamination.
Are the EGR valve and the EGR passage clogged?
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)