DTC P10C5: Proportional valve current(1)
DTC P10C6: Proportional valve current(2)
DTC P10C6: Proportional valve current(2)
| caution | Whenever ECU is replaced, ensure that the CAN bus lines are normal. |
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
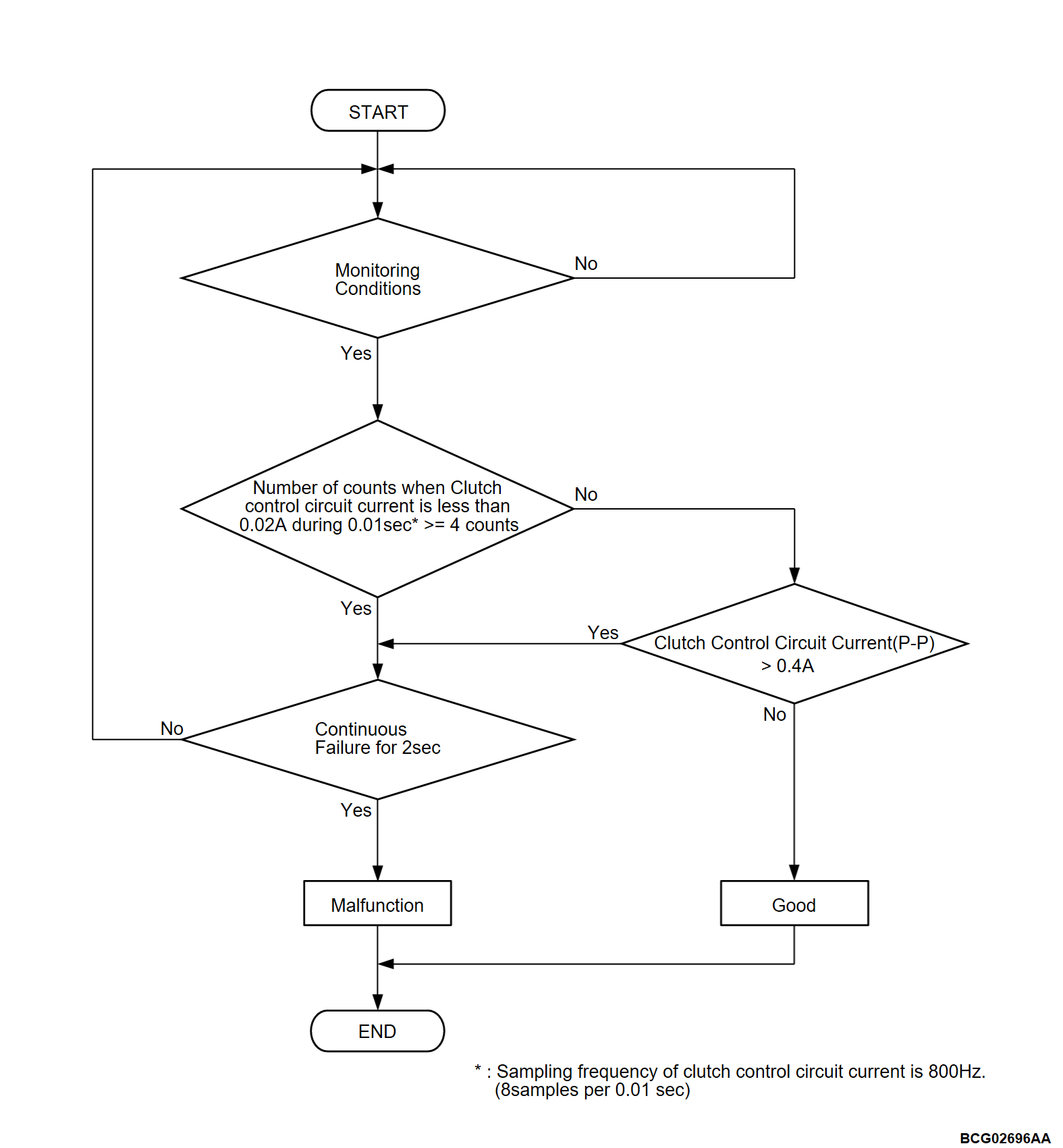
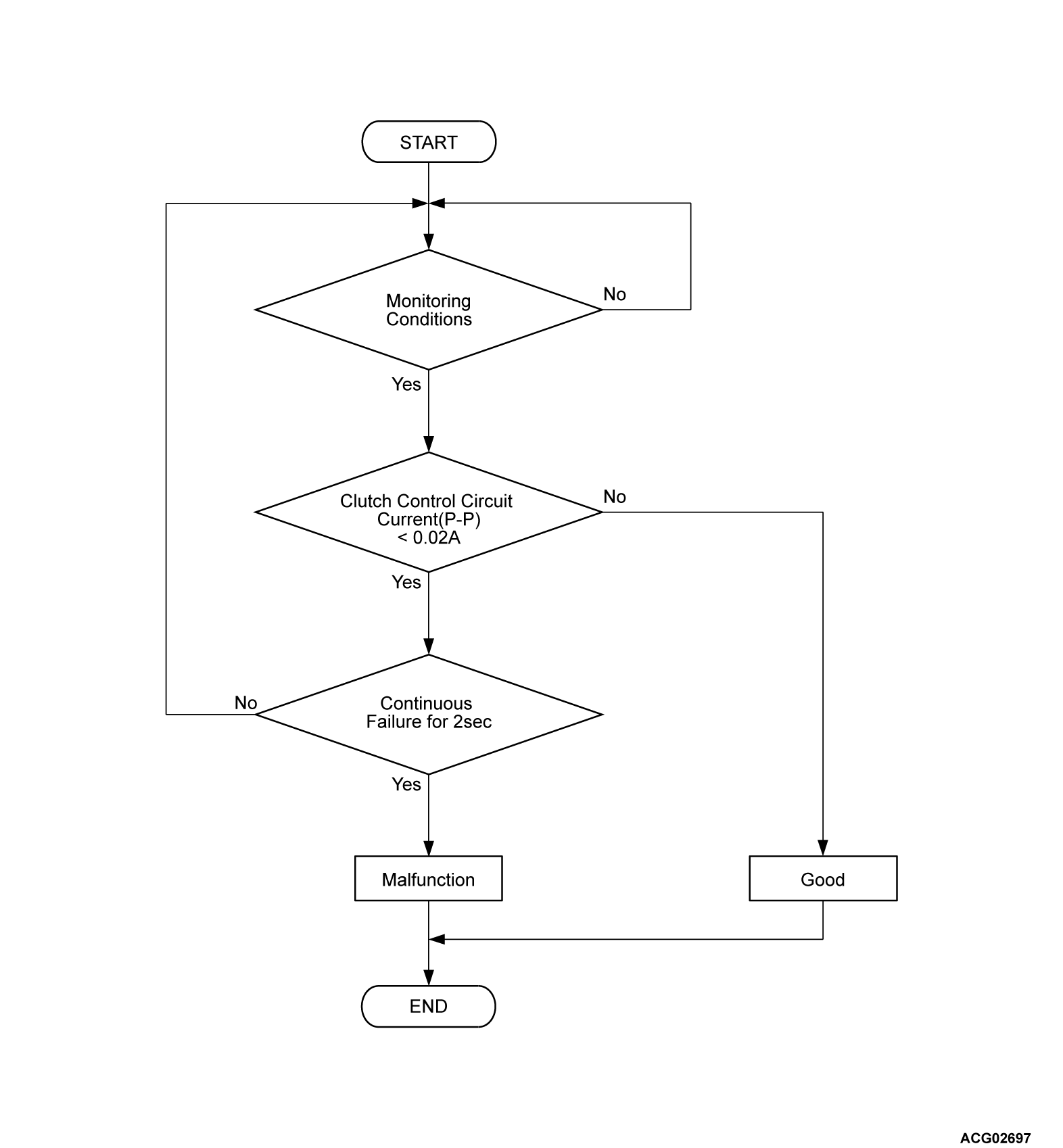
- The clutch control circuit continuously measures the current in the circuit.
- When the circuit is shorted to ground, the amplitude of the waveform increases.
- When the circuit is open or shorted to power supply, the amplitude of the waveform decreases.
MONITOR EXECUTION
Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC stored in memory for the item monitored below)
- Not applicable
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Not applicable
Check Conditions <P10C5>
- The power supply mode of electric motor switch is ON.
- The PHEV-ECU power supply voltage is more than 9.0 volts.
- The operating current of the clutch solenoid valve is 0.05 A or more
Check Conditions <P10C6>
- The power supply mode of electric motor switch is ON.
- The PHEV-ECU power supply voltage is more than 11.0 volts.
- The operating current of the clutch solenoid valve is 0.1 A or less
Judgment Criterion <P10C5>
- When a state with the current of the clutch control circuit being less than 0.02 A occurs 4 times or more in 0.01 seconds continues for 2 seconds
- When a state where the difference between the minimum value and the maximum value of the current of the clutch control circuit is larger than 0.4 A continues for 2 seconds
Judgment Criterion <P10C6>
- When a state where the difference between the minimum value and the maximum value of the current of the clutch control circuit is less than 0.02 A continues for 2 seconds
PROBABLE CAUSES
- The valve body fails (proportional valve fails).
- Damaged harness or connector.
- Malfunction of the PHEV-ECU.
DIAGNOSIS
Required Special Tools
- MB991223: Wiring harness set
- MB992006: Extra fine probe
STEP 1. Proportional valve check.
STEP 2. Check of open and short to ground circuit in the power supply line (PHEV-ECU and proportional valve).
Check the wiring harness between PHEV-ECU connector (terminal SOL) and the proportional valve connector (terminal No.2).
Is the check result normal?
STEP 3. Check of open circuit in the ground line (proportional valve).
Check the wiring harness between proportional valve connector (terminal No.2) and body ground.
Is the check result normal?
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)