DTC P1A1A: FMCU internal fail(2)
| caution | Before replacing the ECU, ensure that the communication circuit is normal. |
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
The torque of the drive motor and the starter generator is monitored by the PHEV-ECU, checking that the drive motor and the starter generator are safely controlled.
MONITOR EXECUTION
Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC stored in memory for the item monitored below)
- Motor/Generator control circuit monitor
- EV-CAN monitor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) current monitor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) coil temperature monitor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) IGBT temperature monitor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) capacitor temperature monitor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) control module temperature monitor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) 3 phase circuit monitor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) inverter voltage monitor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) Control module circuit monitor
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) current sensor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) coil temperature sensor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) position sensor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) IGBT temperature sensor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) capacitor temperature sensor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) control module temperature sensor
- Front electric motor control unit (FEMCU) inverter voltage sensor
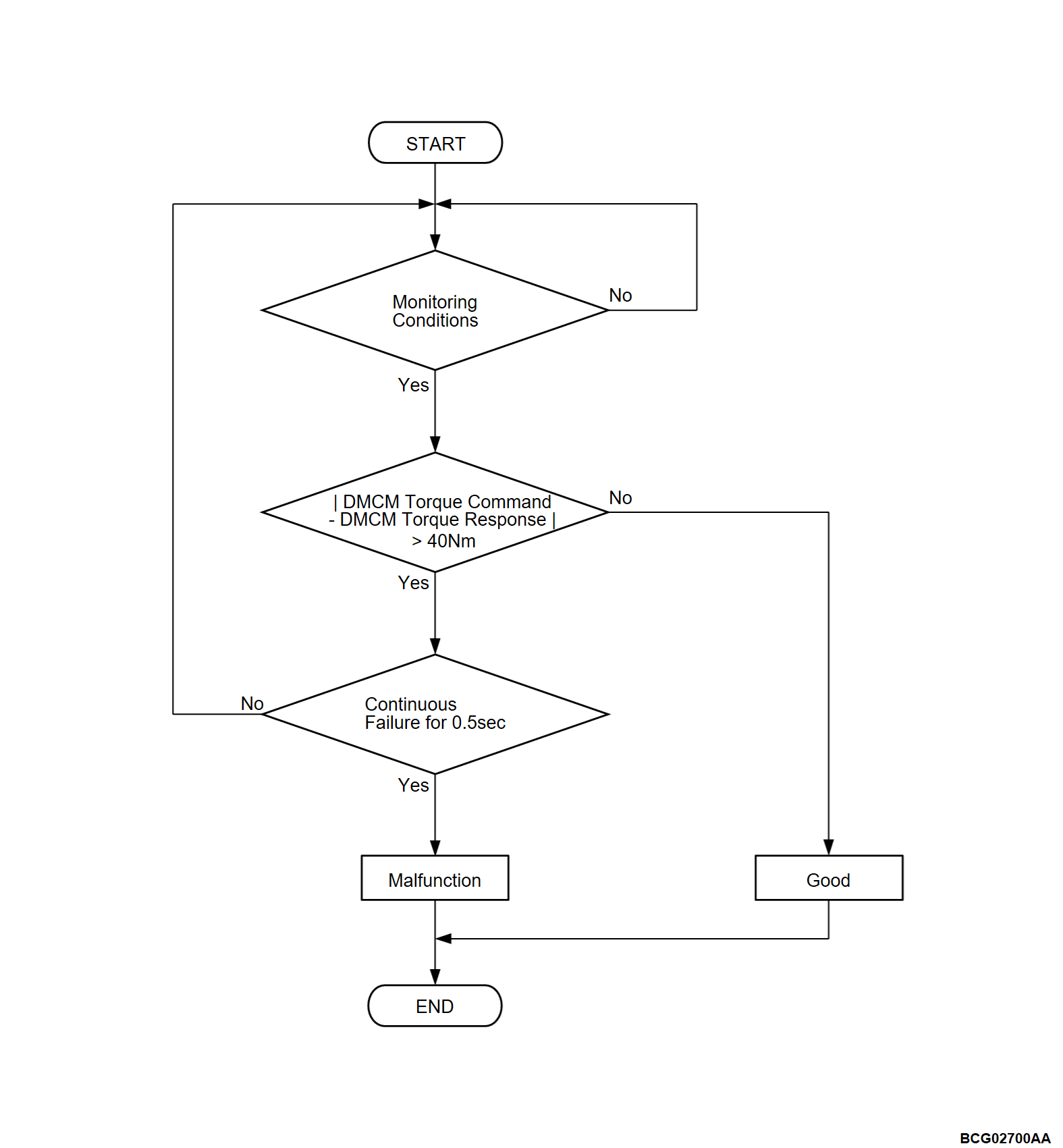
Check Conditions
- The power supply mode of electric motor switch is ON.
- The PHEV-ECU power supply voltage is more than 9.0 volts.
- The absolute value of the command torque of the power drive unit (FEMCU) is less than 200 Nm/sec.
Judgment Criterion
- When a state where the absolute value of the difference between the command torque of the power drive unit (FEMCU) and the response torque of the power drive unit (FEMCU) is larger than 40 Nm continues for 0.5 seconds
PROBABLE CAUSES
Malfunction of the power drive unit (FEMCU).
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check whether the other DTC is set.
Check if any DTC is set in the FEMCU and PHEV-ECU(Refer to GROUP 54Db - Diagnostic Trouble Code Chart  <FEMCU> or
<FEMCU> or  <PHEV-ECU>).
<PHEV-ECU>).
 <FEMCU> or
<FEMCU> or  <PHEV-ECU>).
<PHEV-ECU>).Is the DTC set?
STEP 2. Test the OBD-II drive cycle.
(1) Carry out a test drive with the drive cycle pattern. Refer to Diagnostic Function - OBD-II Drive Cycle - Pattern 1  .
.
 .
.(2) Check the DTC.
Is the DTC set?
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)