DTC P003C: Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing Electronic Control System (MIVEC) Performance Problem
CIRCUIT OPERATION
- A battery positive voltage is applied to the oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch output terminal from the ECM terminal OCVP via the resistor in the ECM.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
- The oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch converts the existence of a engine oil pressure into a high/low voltage, and inputs it into the ECM.
- When the oil feeder control valve operates, the engine oil pressure in the MIVEC system rises. The oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch opens, thus interrupting the application of the battery positive voltage. As a result, the output voltage of the oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch will fluctuate between 0 and 12 volts.
- The ECM checks whether the oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch "OFF" or "ON" during driving.
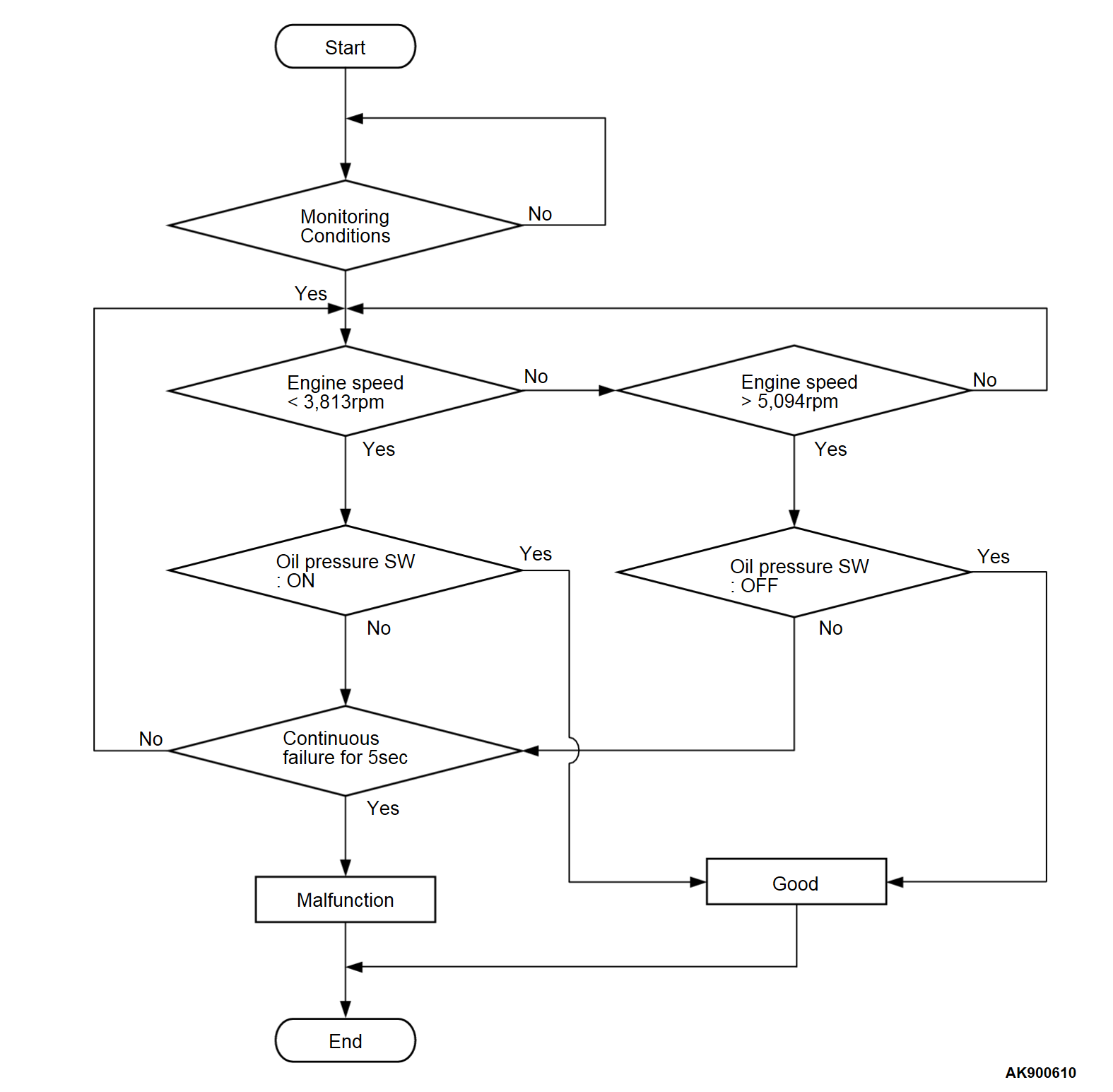
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
- Compare oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch status with engine operating condition.
MONITOR EXECUTION
- Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC stored in memory for the item monitored below)
- Not applicable
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Camshaft position sensor
- Mass airflow sensor
- Engine coolant temperature sensor
- Throttle position sensor
- Injection valve
Check Conditions
- Engine speed is more than 5,094 r/min.
- Engine coolant temperature is 77°C (171 °F) or more.
- Battery positive voltage is between 10 and 16.5 volts.
- 30 seconds or more have passed since the engine starting sequence was completed.
Judgment Criterion
- Oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch (for MIVEC) has been ON for 5 seconds.
FAIL-SAFE AND BACKUP FUNCTION
- Does not switch to high-speed cam.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS (The most likely causes for this code to be stored are: )
- Connector damage.
- Harness damage.
- Oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch failed.
- Oil feeder control valve failed.
- ECM failed.
DIAGNOSIS
Required Special Tools:
- MB992744: Vehicle Communication Interface-Lite (V.C.I.-Lite)
- MB992745: V.C.I.-Lite Main Harness A
- MB992747: V.C.I.-Lite USB Cable Short
- MB992748: V.C.I.-Lite USB Cable Long
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: Vehicles Communication Interface (V.C.I.)
- MB991827: M.U.T.-III USB Cable
- MB991910: M.U.T.-III Main Harness A (Vehicles with CAN communication system)
- MB992110: Power Plant ECU Check Harness
STEP 1. Measure the power supply voltage at ECM connector by using power plant ECU check harness special tool MB992110.
(1) Disconnect all ECM connectors. Connect the power plant ECU check harness special tool MB992110 between the separated connectors.
(2) Start the engine and run at idle.
(3) Measure the voltage between terminal OCVP and ground.
- Voltage should be 1 volt or less when engine is idling.
- Voltage should be battery positive voltage when engine speed is higher than 5,200 r/min.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the measured voltage normal?
STEP 2. Measure the power supply voltage at oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch connector.
(1) Disconnect the oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch connector and measure at the harness side.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(3) Measure the voltage between terminal OCVP line and ground.
- Voltage should be battery positive voltage.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is battery positive voltage (approximately 12 volts) present?
STEP 3. Check of short circuit to ground in OCVP line between oil feeder control valve oil pressure switch connector and ECM connector.
Is the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 4. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-III), check data item 98: Oil feeder control valve.
| caution | To prevent damage to scan tool (M.U.T.-III), always turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position before connecting or disconnecting scan tool (M.U.T.-III). |
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(3) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-III) to the data reading mode for item 98, Oil feeder control valve.
- An operation sound should be heard and vibration should be felt when the oil feeder control valve is operated.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the oil feeder control valve operating properly?
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)