DTC P264C: Variable Valve Lift Sensor Circuit Low Input
CIRCUIT OPERATION
- A power voltage of 5 V is applied to the variable valve lift sensor from the ECM terminal VLS5.
- The power voltage is grounded to the ECM terminal VLSE from the variable valve lift sensor.
- The sensor signal is inputted to the ECM terminal VLS from the variable valve lift sensor output terminal.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
- The variable valve lift sensor converts valve lift amount to voltage signal, and then sends it to the ECM.
- The ECM uses this signal to control the valve lift mount.
MONITOR EXECUTION
- Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC stored in memory for the item monitored below)
- Variable valve lift system monitor
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Not applicable
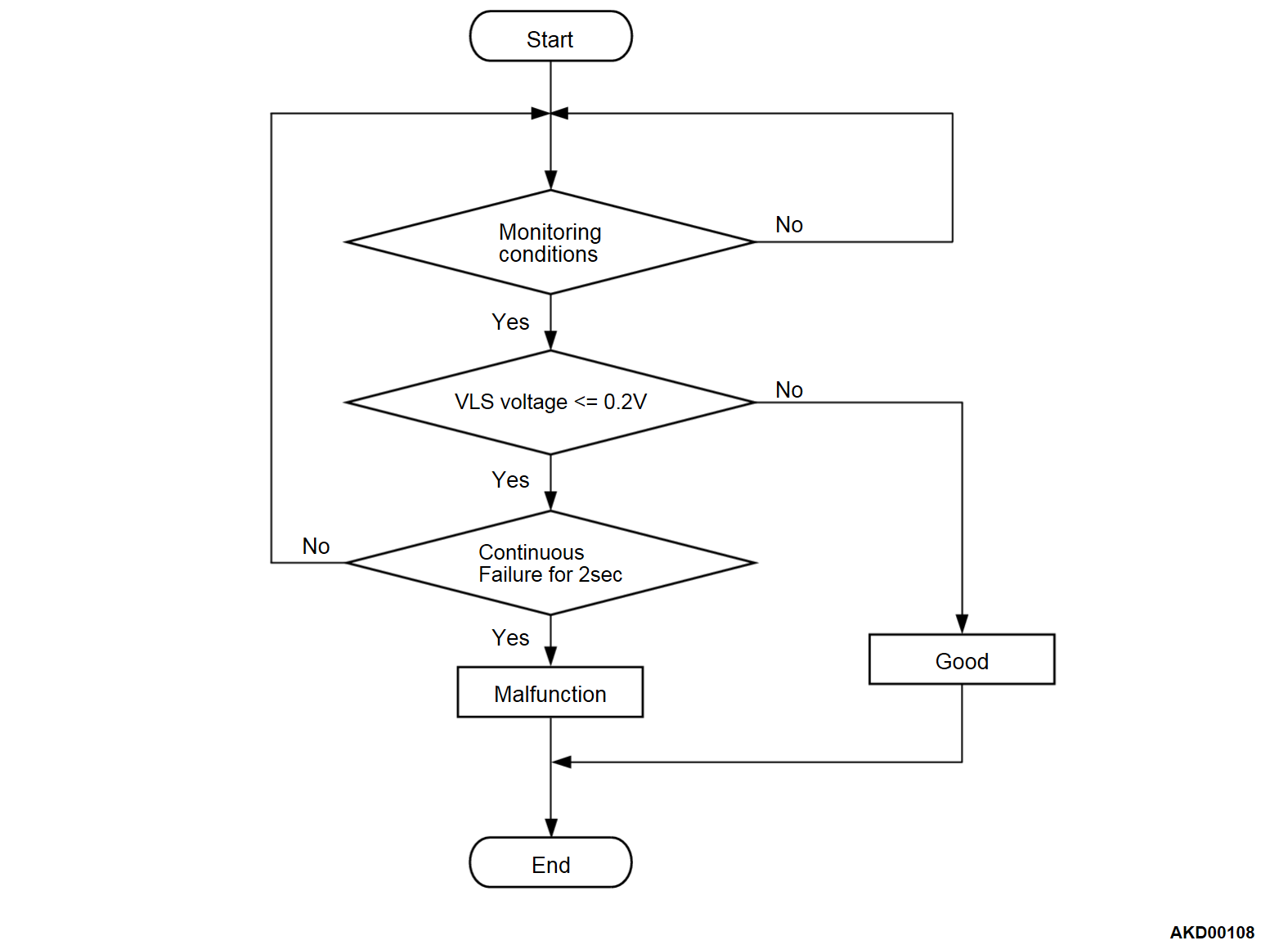
DTC SET CONDITIONS
Check Conditions
- More than 2 seconds have passed since the engine starting sequence was completed.
- Battery positive voltage is between 10 and 16.5 volts.
Judgment Criteria
- Variable valve lift sensor output voltage is less than 0.2 volt for 2 seconds.
FAIL-SAFE AND BACKUP FUNCTION
- The valve lift is fixed to maximum. Otherwise, deenergizes the motor.
- V.V.T. phase angle is set to most retarded position.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS (The most likely causes for this code to be stored are: )
- Variable valve lift sensor failed.
- Open or shorted variable valve lift sensor circuit, harness damage, or connector damage.
- ECM failed.
DIAGNOSIS
Required Special Tools:
- MB992744: Vehicle communication interface-Lite (V.C.I.-Lite)
- MB992745: V.C.I.-Lite main harness A
- MB992747: V.C.I.-Lite USB cable short
- MB992748: V.C.I.-Lite USB cable long
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: Vehicles Communication Interface (V.C.I.)
- MB991827: M.U.T.-III USB Cable
- MB991910: M.U.T.-III Main Harness A (Vehicles with CAN communication system)
STEP 1. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-III), check data list item 170: Variable Valve Lift Sensor.
| caution | To prevent damage to scan tool (M.U.T.-III), always turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position before connecting or disconnecting scan tool (M.U.T.-III). |
(2) Start the engine and run at idle.
(3) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-III) to the data reading mode for item 170, Variable Valve Lift Sensor.
(4) Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature: 80°C to 95°C (176°F to 203°F).
- Output voltage should be between 0.2 and 4.8 volts (depends on engine operation condition).
(5) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 2. Measure the sensor supply voltage at variable valve lift sensor harness side connector.
(1) Disconnect the variable valve lift sensor connector and measure at the harness side.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(3) Measure the voltage between terminal VLS5 line and ground.
- Voltage should be between 4.9 and 5.1 volts.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the measured voltage between 4.9 and 5.1 volts?
STEP 3. Check of short to ground and open circuit in VLS5 line between variable valve lift sensor connector and ECM connector.
Is the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 4. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-III), check data list item 170: Variable Valve Lift Sensor.
(1) Start the engine and run at idle.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-III) to the data reading mode for item 170, Variable Valve Lift Sensor.
(3) Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature: 80°C to 95°C (176°F to 203°F).
- Output voltage should be between 0.2 and 4.8 volts (depends on engine operation condition).
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 5. Check of harness damage in VLS5 line between variable valve lift sensor connector and ECM connector.
Is the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 6. Check of short to ground, open circuit and harness damage in VLS line between variable valve lift sensor connector and ECM connector.
Is the harness wire in good condition?
STEP 7. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-III), check data list item 170: Variable Valve Lift Sensor.
(1) Start the engine and run at idle.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-III) to the data reading mode for item 170, Variable Valve Lift Sensor.
(3) Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature: 80°C to 95°C (176°F to 203°F).
- Output voltage should be between 0.2 and 4.8 volts (depends on engine operation condition).
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 8. Replace the variable valve lift sensor.
(1) Replace the variable valve lift sensor.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(3) After the DTC has been deleted, read the DTC again.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is DTC P264C stored?
 The inspection is complete.
The inspection is complete.![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)