SYMPTOM CHART
| warning | When touching the throttle valve, surely shut off the driving circuits of the throttle valve. In the event that the throttle valve is operated, a finger might be injured as the result of being caught by the throttle valve. |
| caution | During diagnosis, a DTC associated with other systems may be stored when the ignition switch is turned on with connector(s) disconnected. On completion, confirm all systems for DTC(s). If DTC(s) are stored, erase them all. |
| caution | Disconnecting the battery cables or removing the combination meter will erase the learned value of the fuel gauge. To recover the learned value, input a vehicle speed (by actually driving the vehicle or inputting a simulated vehicle speed), and stop the vehicle. This will complete the learning process. |
| note | Check that the ECM ground circuit is normal before checking for the cause of the problem. |
| note | When the racing (2,000 to 5,000 r/min or more) continues on the vehicle stopped with no load during the specified time or more, the increase in the engine speed might be limited. This comes from the engine protection and control functions and is not a malfunction. |
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE (FOR YOUR INFORMATION)
| ITEMS | SYMPTOM | ||
| At starting | Won't start | The starter cranks the engine, but there is no combustion within the cylinders, and the engine won't start. | |
| Starts up and dies | The engine starts, but then engine soon stalls. | ||
| Hard starting | Engine starts after cranking a while. | ||
| Idling stability | Hunting | Engine speed doesn't remain constant; changes at idle. | |
| Rough idle | Usually, a judgment can be based upon the movement of the tachometer pointer, and the vibration transmitted to the steering wheel, shift lever, body, etc. | ||
| Incorrect idle speed | The engine doesn't idle at the correct speed. | ||
| Engine stall (die out) | The engine stalls when the foot is taken from the accelerator pedal, regardless of whether the vehicle is moving or not. | ||
| Engine stall (pass out) | The engine stalls when the accelerator pedal is depressed. | ||
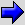
| At driving | Hesitation Sag | "Hesitation" is the delay in response of the vehicle speed (engine speed). This occurs when the accelerator is depressed in order to accelerate from the speed at which the vehicle is now traveling, or a temporary drop in vehicle speed (engine speed) during such acceleration. Serious hesitation is called "sag". | |
| Poor acceleration | Poor acceleration is inability to obtain an acceleration corresponding to the degree of throttle opening, even though acceleration is smooth. Also the inability to reach maximum speed. | ||
| Stumble | Engine speed increase is delayed when the accelerator pedal is initially depressed for acceleration. | ||
| Shock | The feeling of a comparatively large impact or vibration when the engine is accelerated or decelerated. | ||
| Surge | This is slight acceleration and deceleration feel usually felt during steady, light throttle cruise. Most notable under light loads. | ||
| Knocking | A sharp sound during driving, which sounds like a hammer striking the cylinder walls. It makes poor driveability. | ||
| At stopped | Run on ("Dieseling") | The condition in which the engine continues to run after the ignition switch is turned to the "LOCK" (OFF) position. Also called "dieseling". | |
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)