DTC P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
- If a misfire occurs while the engine is running, the engine speed changes for an instant.
- The ECM checks for such changes in engine speed.
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
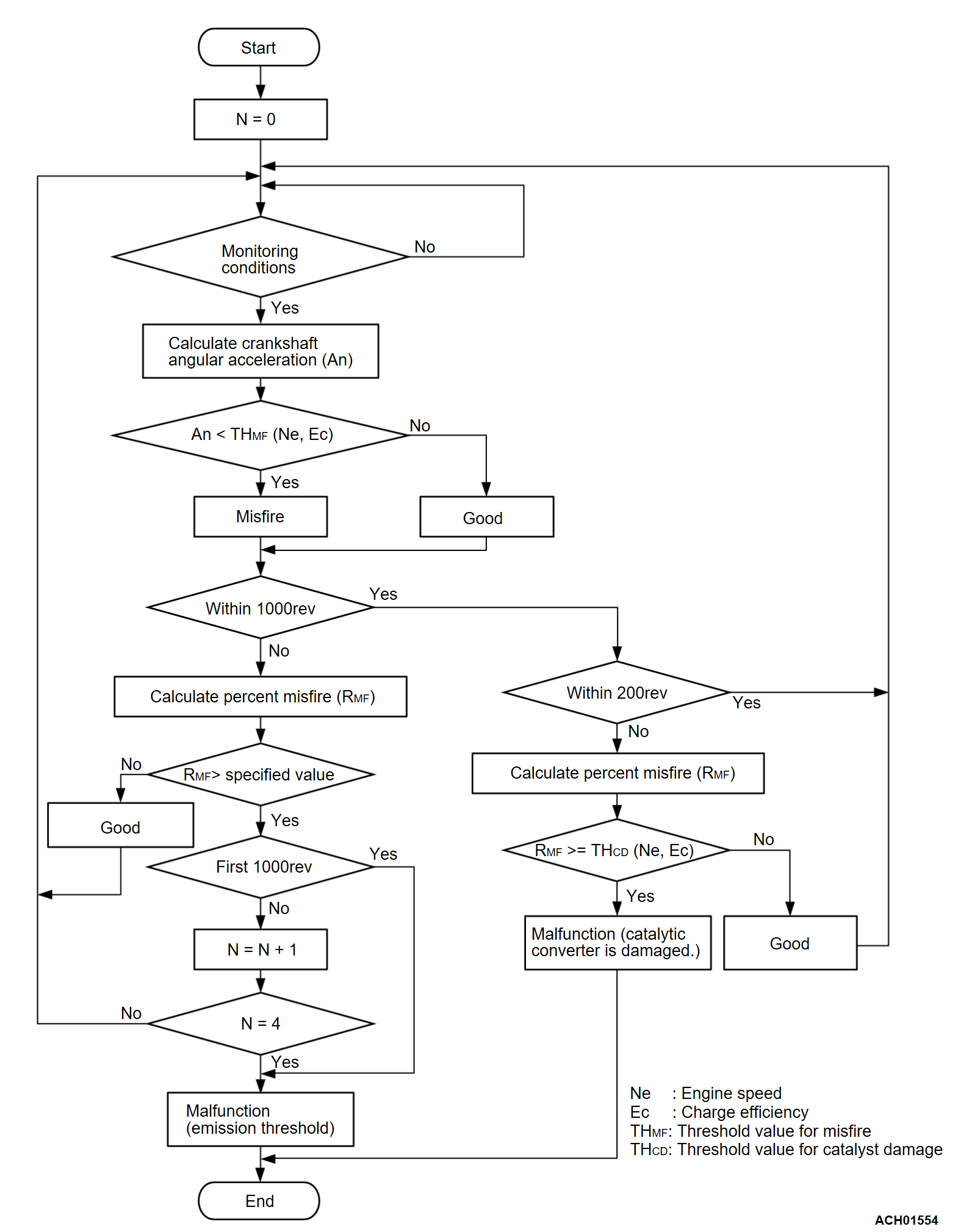
- Monitor angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect malfunction when negative variation of the angular acceleration is large.
MONITOR EXECUTION
- Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC set in memory for the item monitored below)
- Not applicable
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Camshaft position sensor
- Mass airflow sensor
- Engine coolant temperature sensor
- Intake air temperature sensor 1
- Barometric pressure sensor
- Throttle position sensor
DTC SET CONDITIONS
Check Conditions
- Engine speed is between 438 and 6,313 r/min.
- Engine coolant temperature is more than -10°C (14°F). (However, 20°C (68°F) when the engine coolant temperature at engine start is -10°C (14°F) or less).
- Barometric pressure is more than 76 kPa (22.4 in.Hg).
- The engine load is with in the positive torque load.
- Adaptive learning is complete for the vane which generates a crankshaft position signal.
- While the engine is running, excluding sudden acceleration/deceleration and fuel shut-off operation.
Judgment Criterion (change in the angular acceleration of the crankshaft is used for misfire detection)
- Misfire has occurred more frequently than allowed during the last 200 revolutions [when the catalyst temperature is more than 980°C (1,796°F)].
or
- Misfire has occurred more than in 2.0 percent of the first 1,000 revolutions (corresponding to 1.5 times the limit of emission standard).
or
- After the first 1,000 revolutions, the following criterion is satisfied 4 times cumulatively.
- Misfire counts per 1,000 revolutions exceeds in 2.0 percent (corresponding to 1.5 times the limit of emission standard).
FAIL-SAFE AND BACKUP FUNCTION
- The supply of fuel to the misfiring cylinder can possibly be cut.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS (The most likely causes for this code to be set are: )
- Ignition system related part(s) failed.
- Crank angle sensor failed.
- Injector failed.
- Incorrect air/fuel ratio.
- Low compression pressure.
- Intake air temperature sensor 1 failed.
- Engine coolant temperature sensor failed.
- Mass airflow sensor failed.
- Skipping of timing chain teeth.
- ECM failed.
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 2: Crankshaft Position Sensor.
| caution | To prevent damage to scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), always turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position before connecting or disconnecting scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE). |
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(3) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 2, Crankshaft Position Sensor.
- The tachometer and engine speed indicated on the scan tool should match.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 2. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 5: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 5, Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1.
- The intake air temperature and temperature shown with the scan tool should approximately match.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 3. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 6: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 6, Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor.
- The engine coolant temperature and temperature shown with the scan tool should approximately match.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 4. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 10: Mass Airflow Sensor.
(1) Start the engine and run at idle.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 10, Mass Airflow Sensor.
(3) Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature: 80°C to 95°C (176°F to 203°F).
- The standard value during idling should be between 800 and 1,120 millivolts.
- When the engine is revved, the mass airflow rate should increase according to the increase in engine speed.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the sensor operating properly?
STEP 5. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 26: Long-Term Fuel Trim.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 26, Long-Term Fuel Trim.
- The fuel trim should be between -12.5 and +12.5 percent.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the specification normal?
STEP 6. Using scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE), check data list item 28: Short-Term Fuel Trim.
(1) Start the engine and run at idle.
(2) Set scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to the data reading mode for item 28, Short-Term Fuel Trim.
- The fuel trim should be between -25 and +25 percent when the engine is 2,500 r/min (during closed loop) after the engine is warmed.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Is the specification normal?
STEP 7. Visual check of ignition spark.
(1) Remove the spark plug and install it to the ignition coil.
(2) Connect the ignition coil connector.
(3) Disconnect all injector connectors.
(4) At the engine start, check each spark plug produces a spark.
Did it spark?
STEP 9. Check air intake from intake hose and intake manifold.
STEP 11. Check for skipped timing chain teeth.
STEP 12. Check the compression.
STEP 13. Replace the ECM.
(2) Carry out a test drive with the drive cycle pattern. Refer to Diagnostic Function - OBD-II Drive Cycle - Pattern 17  .
.
 .
.(3) Check the diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
Is DTC P0300 set?
 Check for foreign matters (water, diesel fuel, etc.) in fuel and replace if necessary. Then go to Step 14.
Check for foreign matters (water, diesel fuel, etc.) in fuel and replace if necessary. Then go to Step 14.
 The inspection is complete
The inspection is complete![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)