DTC P0796: Abnormality in Primary Pressure Solenoid Valve Function
DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION
If the actual pulley ratio does not track with the target ratio, the TCM determines whether the system is faulty.
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
- If the actual pulley ratio remains 2.0 to 2.55 for 5 seconds when the target pulley ratio is 1.2 or less, or if the actual pulley ratio remains 0.2 to 0.75 for 5 seconds when the target pulley ratio is 1.55 or more, the TCM determines that a malfunction exists.
MONITOR EXECUTION
- Transmission range: "D", "R" or "L"
- Engine speed: 450 r/min or more
- Primary pulley speed: 306 r/min or more
- Secondary pulley speed: 230 r/min or more
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (OTHER MONITOR AND SENSOR)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC stored in memory for the item monitored below)
- P0705: Malfunction of transmission range switch
- P0715: Malfunction of primary pulley speed sensor
- P0746: Abnormality in hydraulic control system
- P0791: Malfunction of the secondary pulley speed sensor
- P0842, P0843: Malfunction of the secondary pressure sensor
- P0962, P0963: Malfunction of the line pressure solenoid valve
- P0970, P0971: Malfunction of the primary pressure solenoid valve
- U0001: Malfunction of CAN communication
- U0100: CAN time-out error (engine)
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Transmission range switch
- Primary pulley speed sensor
- Secondary pulley speed sensor
- Secondary pressure sensor
- Line pressure solenoid valve
- Primary pressure solenoid valve
DTC SET CONDITIONS
Check Conditions
- Transmission range switch position: "D", "R" or "L"
- Engine speed: 450 r/min or more
- Primary pulley speed: 306 r/min or more
- Secondary pulley speed: 230 r/min or more
Judgment Criteria
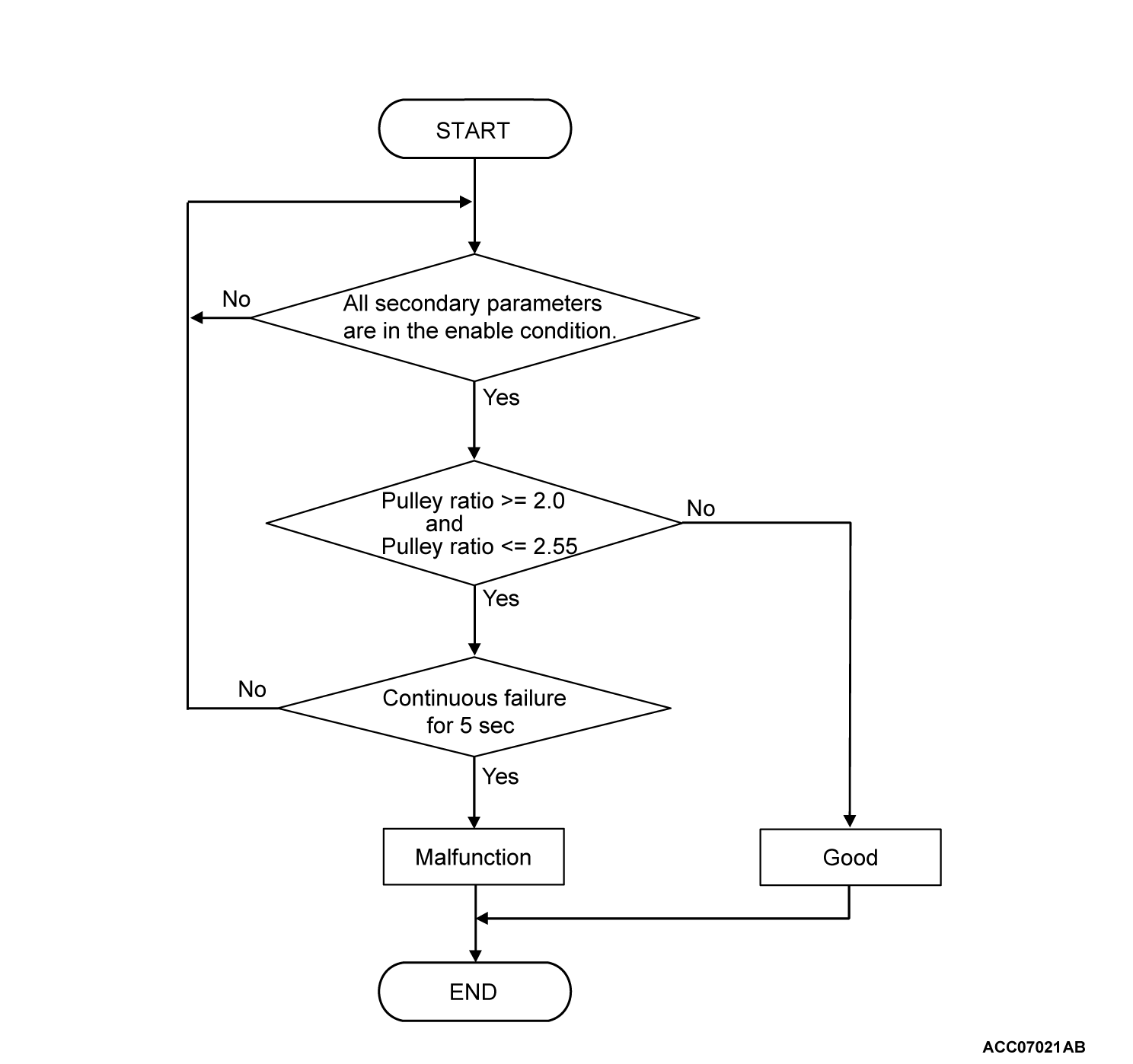
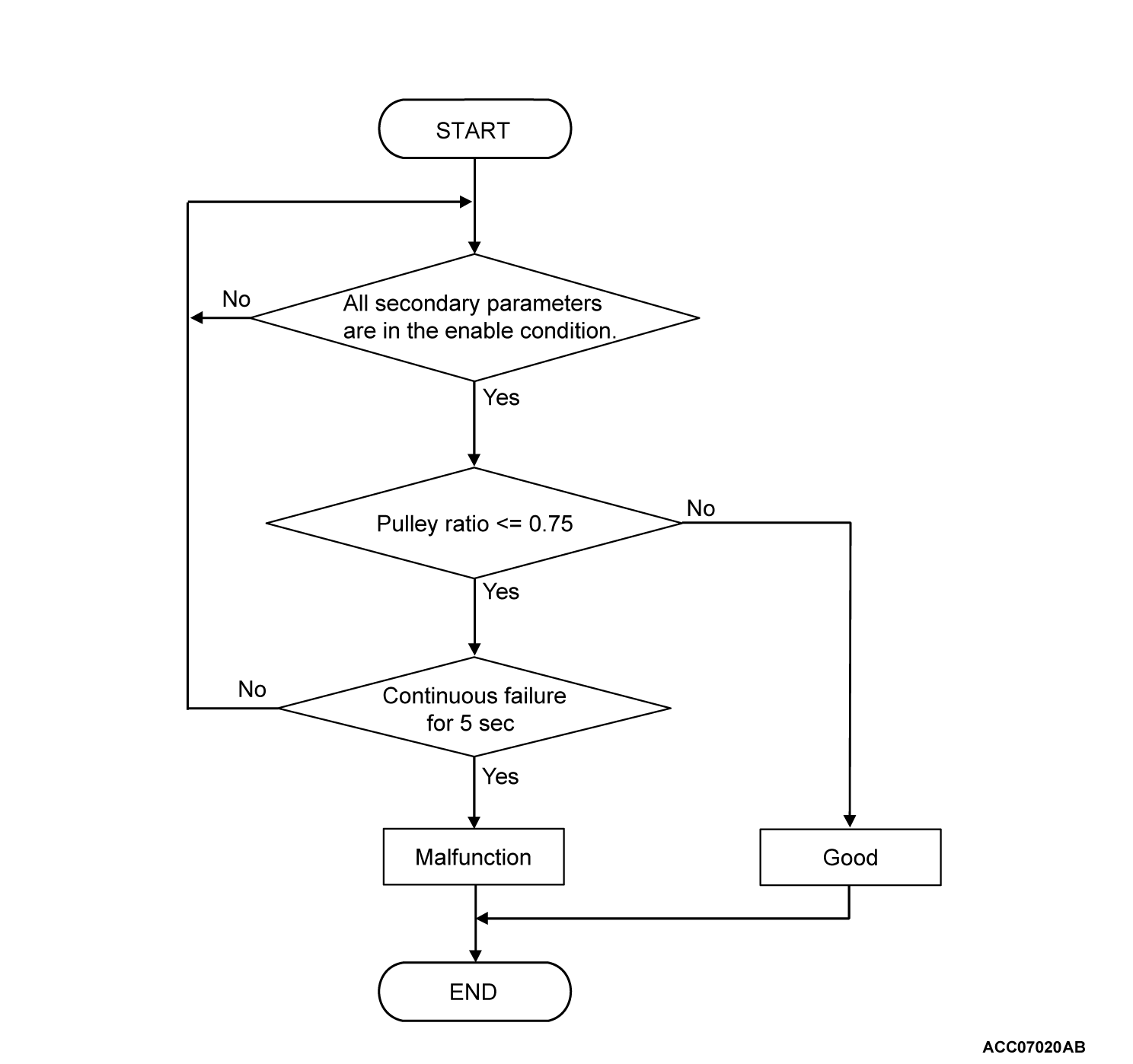
- When the target pulley ratio (primary pulley speed/secondary pulley speed) is less than 1.2 while the vehicle is being driven, the actual pulley ratio remains from 2.0 to 2.55 for 5 seconds.
- When the target pulley ratio (primary pulley speed/secondary pulley speed) is more than 1.55 while the vehicle is being driven, the actual pulley ratio remains from 0.75 or less for 5 seconds.
OBD-II DRIVE CYCLE PATTERN
The vehicle is driven for at least 10 seconds with the accelerator opening angle at 20 percent or more.
PROBABLE CAUSES
- Malfunction of the valve body assembly (Faulty line pressure solenoid valve)
- Malfunction of the transaxle assembly
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check the following connector.
- CVT assembly connector
Check the terminals for a contact status problem and internal short circuit.
Is the check result normal?
 Repair the faulty connector.
Repair the faulty connector.STEP 2. Measure the output wave pattern of the primary pressure solenoid valve at TCM connector (PRLS terminal).
(1) Connect the CVT assembly connector.
(2) Transmission range: "P" range
(3) Engine: Idling
(4) Connect an oscilloscope, and measure the voltage between TCM connector PRLS terminal and body ground.
Is the check result normal?
STEP 3. Symptom recheck after erasing DTC.
(1) Erase the DTC.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position, and then wait for one minute. Then drive the vehicle until the engine has been warmed up.
(3) Check if the DTC is stored.
Is the DTC stored?
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)