| Communication with scan tool is impossible | Communication with ECM is not possible | 1 |  |
| Malfunction Indicator Light (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or Check Engine Light) and related parts | The Malfunction Indicator Light (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or Check Engine Light) does not illuminate right after the ignition switch is turned to the "ON" position | 2 |  |
| The Malfunction Indicator Light (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or Check Engine Light) remains illuminated and never goes out | 3 |  |
| Starting | Cranks, won't start | 4 |  |
| Starts up and dies | 5 |  |
| Hard starting | 6 |  |
| Idling stability (improper idling) | Unstable idle (rough idle, hunting) | 7 |  |
| Idle speed is high (improper idle speed) | 8 |  |
| Idle speed is low (improper idle speed) | 9 |  <M/T>, <M/T>,  <CVT> <CVT> |
| Idling stability (engine stalls) | When the engine is cold, it stalls at idle (die out) | 10 |  |
| When the engine is hot, it stalls at idle (die out) | 11 |  |
| The engine stalls when accelerating (pass out) | 12 |  |
| The engine stalls when decelerating | 13 |  |
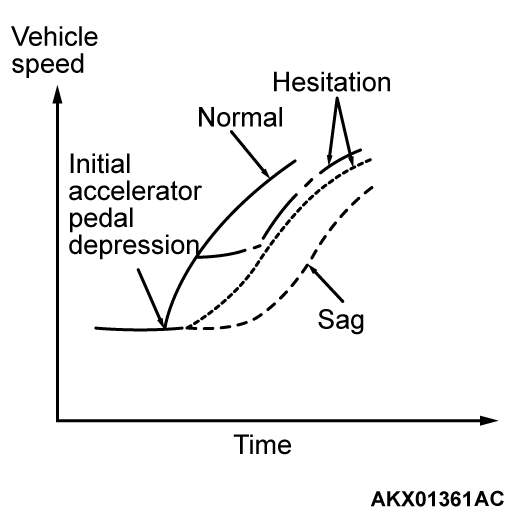
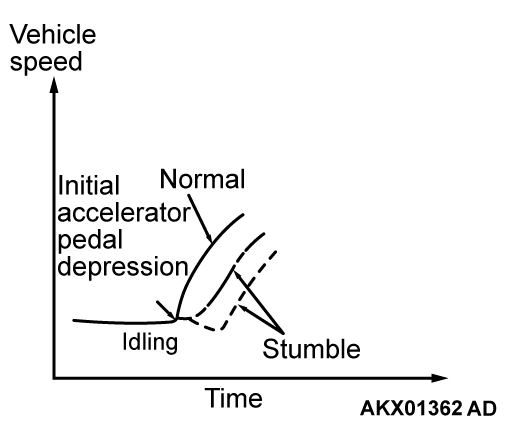
| Driving | Hesitation, sag, stumble, poor acceleration or surge | 14 |  |
| Acceleration shock | 15 |  |
| Knocking | 16 |  |
| Dieseling (run-on) | 17 |  |
| Too high CO and HC concentration when idling | 18 |  |
| IM240 test failure | Transient, mass emission tailpipe test failure | 19 |  |
| Purge flow test of the evaporative emission canister failure | 20 |  |
| Pressure test of the evaporative system failure | 21 |  |
| Power supply system and ignition switch-IG system | 22 |  |
| Fuel pump system | 23 |  |
| Ignition switch-ST system and starter relay system <M/T> | 24 |  |
| Ignition switch-ST system and starter relay system <CVT> | 25 |  |
| Ignition circuit system | 26 |  |
| A/C switch system <Manual A/C> | 27 |  |
| A/C compressor relay system | 28 |  |
| Fan control relay system | 29 |  |
| Blower fan signal system <Manual A/C> | 30 |  |
| Defogger switch system <Manual A/C> | 31 |  |
| Brake monitoring switch system | 32 |  |
| Engine oil pressure switch system | 33 |  |
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)