Inspection
INSPECTION AFTER REMOVAL
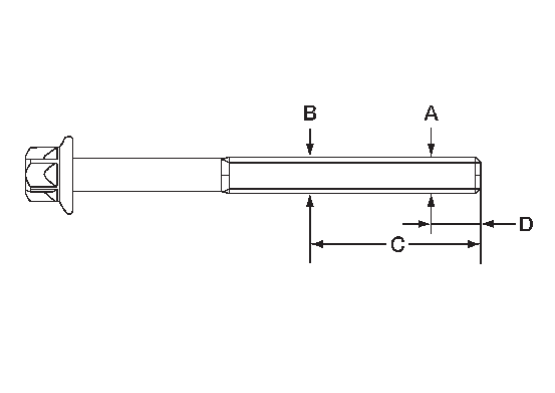
Cylinder Head Bolts Outer Diameter
Cylinder Head Distortion
| note | When performing this inspection, cylinder block distortion should also be checked. Refer to Inspection . . |
1. Wipe off engine oil and remove water scale deposits, old gasket, old sealer, and carbon using a suitable tool.
| caution | Use care not to allow gasket debris to enter passages for engine oil or engine coolant. |
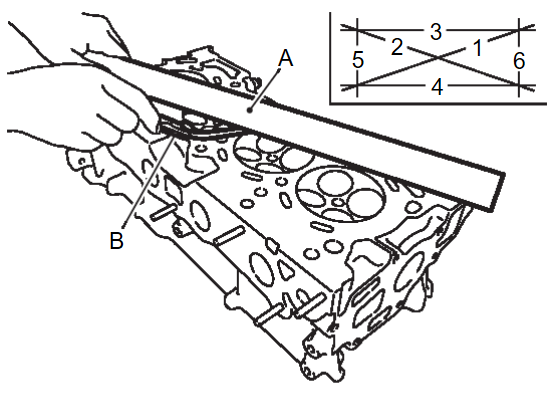
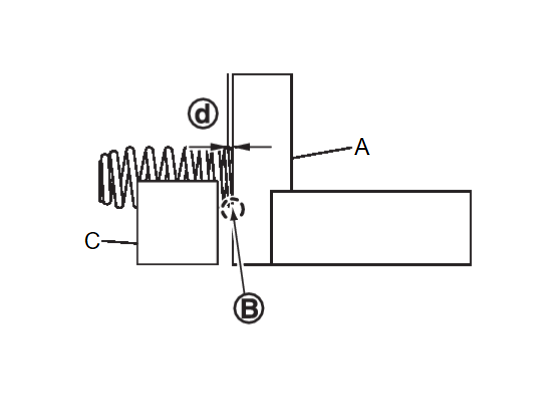
2. At each of several locations on bottom surface of cylinder head, measure the distortion in six directions.
| A | : Straightedge |
| B | : Feeler gauge |
| Limit | : Refer to Cylinder HeadCylinder Head . . |
- If it exceeds the limit, replace cylinder head.
VALVE DIMENSIONS
- Check dimensions of each valve. For dimensions, refer to Cylinder HeadCylinder Head
 .
. - If dimensions are out of the standard, replace valve.
VALVE GUIDE CLEARANCE
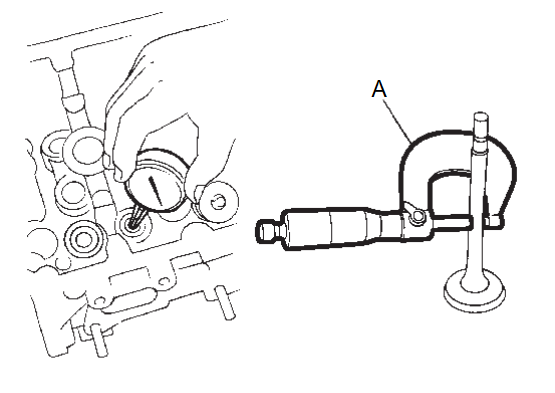
Valve Stem Diameter
Measure the diameter of valve stem with a micrometer (A).
| Standard | : Refer to Cylinder HeadCylinder Head . . | |
Valve Guide Inner Diameter
Measure the inner diameter of valve guide with a bore gauge.
| Standard | : Refer to Cylinder HeadCylinder Head . . | |
Valve Guide Clearance
(Valve guide clearance) = (Valve guide inner diameter) – (Valve stem diameter).
| Standard and Limit | : Refer to Cylinder HeadCylinder Head . . | |
- If it exceeds the limit, replace valve guide and/or valve. When valve guide must be replaced. Refer to Disassembly and Assembly
 .
.
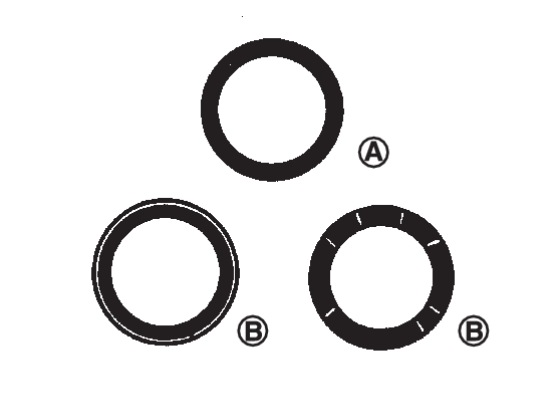
VALVE SEAT CONTACT
- After confirming that the dimensions of valve guides and valves are within specifications, perform this procedure.
- Apply prussian blue (or white lead) onto contacting surface of valve seat to check the condition of the valve contact on the surface.
- Check if the contact area band is continuous all around the circumference.

: OK 
: NG - If not, grind to adjust valve fitting and check again. If the contacting surface still has NG conditions even after the re-check, replace valve seat. Refer to Disassembly and Assembly
 .
.
VALVE SPRING SQUARENESS
- Set try square (A) along the side of valve spring and rotate the spring. Measure the maximum clearance
 between the top of valve spring and try square.
between the top of valve spring and try square.
: Contact C : V-block caution Never remove valve spring seat from valve spring. Limit : Refer to Cylinder HeadCylinder Head  .
. - If it exceeds the limit, replace valve spring (with valve spring seat).
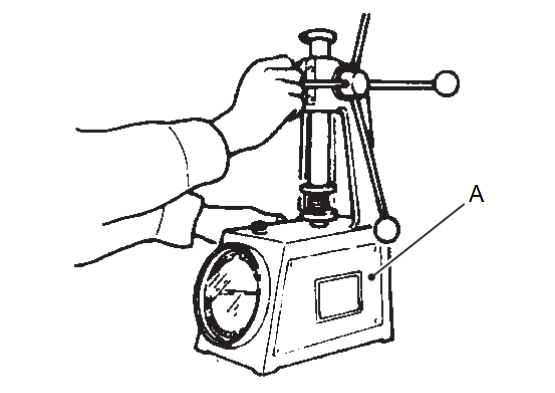
VALVE SPRING DIMENSIONS AND VALVE SPRING PRESSURE LOAD
| caution | Do not remove the valve spring seat. |
- Check valve spring pressure with valve spring seat installed at the specified spring height.
A : Valve spring tester note Before measuring valve spring pressure, compress each spring to specified solid height for intake and exhaust valve springs. Valve spring : 24.76 mm (0.9748 in) Standard : Refer to Cylinder HeadCylinder Head  .
. - If the installation load or load with valve open is out of the standard, replace valve spring (with valve spring seat).
INSPECTION AFTER INSTALLATION
Inspection for Leaks
The following are procedures for checking fluids leak, lubricates leak and exhaust gases leak.
- Before starting engine, check oil/fluid levels including engine coolant and engine oil. If less than required quantity, fill to the specified level. Refer to Fluids and Lubricants
 .
. - Use procedure below to check for fuel leakage.
- Turn ignition switch “ON” (with engine stopped). With fuel pressure applied to fuel piping, check for fuel leakage at connection points.
- Start engine. With engine speed increased, check again for fuel leakage at connection points.
- Run engine to check for unusual noise and vibration.
note If hydraulic pressure inside timing chain tensioner drops after removal/installation, slack in guide may generate a pounding noise during and just after the engine start. However, this does not indicate an unusualness. Noise will stop after hydraulic pressure rises. - Warm up engine thoroughly to check there is no leakage of fuel, exhaust gases, or any oil/fluids including engine oil and engine coolant.
- Bleed air from lines and hoses of applicable lines, such as in cooling system.
- After cooling down engine, again check oil/fluid levels including engine oil and engine coolant. Refill to the specified level, if necessary.Summary of the inspection items:
Items Before starting engine Engine running After engine stopped Engine coolant Level Leakage Level Engine oil Level Leakage Level Transmission / transaxle fluid AT & CVT Models Leakage Level / Leakage Leakage MT Models Level / Leakage Leakage Level / Leakage Other oils and fluids* Level Leakage Level Fuel Leakage Leakage Leakage Exhaust gases — Leakage — *: Power steering fluid, brake fluid, etc.
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)