DTC P0AE6: Pre-charge contactor circuit low
| caution | Before replacing the ECU, ensure that the communication circuit is normal. |
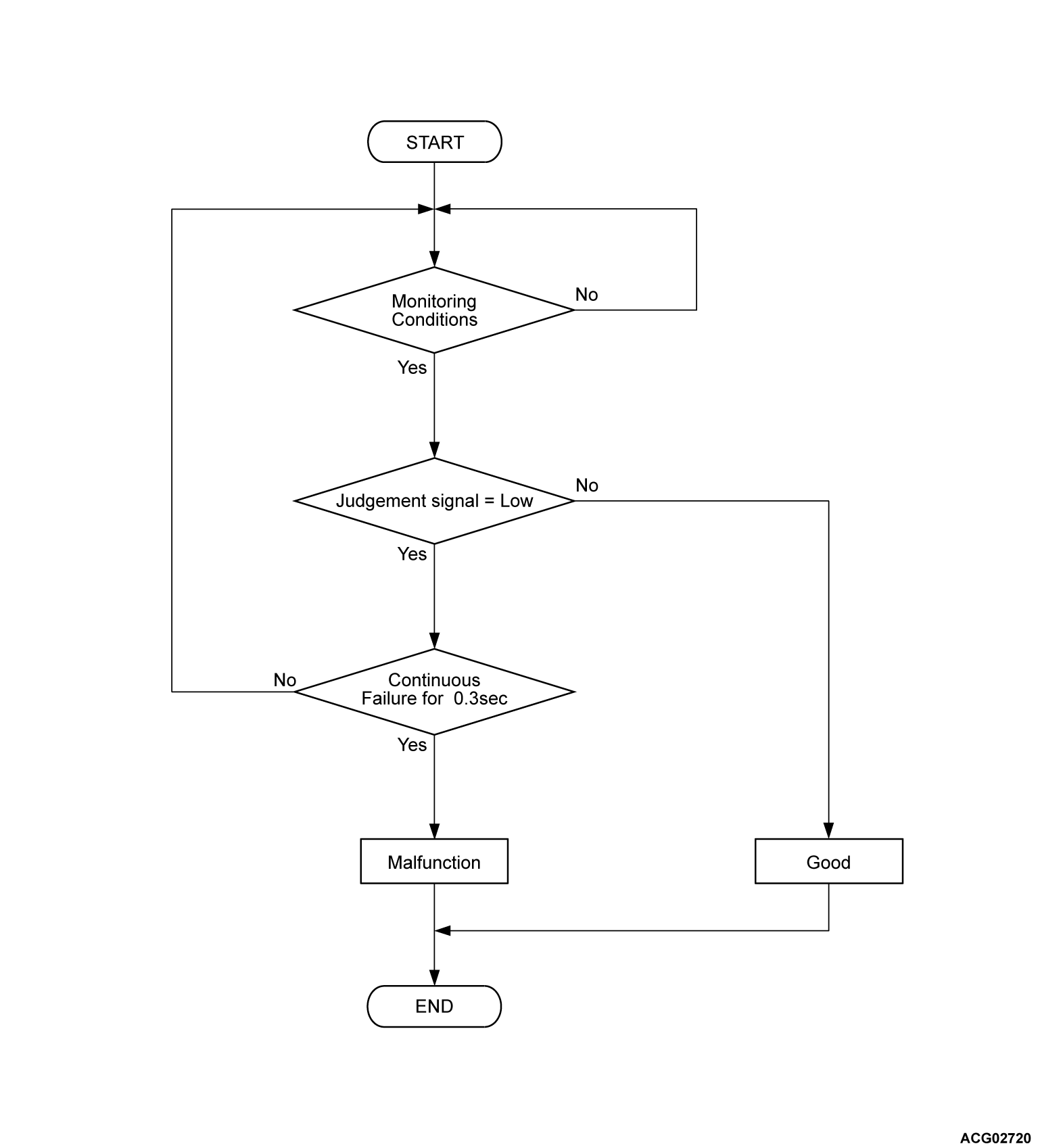
DESCRIPTIONS OF MONITOR METHODS
- Contactor excitation circuit status is judged by voltage and current of an intelligent power device (IPD) in the PHEV-ECU.
- Each fail is judged under the following conditions.
- Charging contactor control circuit shorted low: Charging contactor control circuit active command on.
- Charging contactor control circuit open/shorted high: Charging contactor control circuit active command is off.
MONITOR EXECUTION
- Continuous
MONITOR EXECUTION CONDITIONS (Other monitor and Sensor)
Other Monitor (There is no temporary DTC stored in memory for the item monitored below)
- Not applicable
Sensor (The sensor below is determined to be normal)
- Not applicable
DTC SET CONDITIONS
Check Conditions
- The PHEV-ECU power supply voltage is more than 9.0 volts.
- The charging contactor activation command on.
Judgment Criterion
- Judgment signal from intelligent power device (IPD) for charging contactor is low for 0.3 second.
PROBABLE CAUSES
- Damaged harness or connector.
- Malfunction of the charging contactor.
- Malfunction of the PHEV-ECU.
DIAGNOSIS
Required Special Tools
- MB991223: Wiring harness set
- MB992006: Extra fine probe
STEP 1. Check the signal line for short to ground circuit (PHEV-ECU connector and main drive lithium-ion battery connector).
(1) Disconnect the connector and measure at the harness connector side.
(2) Check the wiring harness between PHEV-ECU connector (terminal CNTP) and the main drive lithium-ion battery connector.
Is the check result normal?
STEP 2. Check the CNTB wire between the IGCT relay connector terminal and the PHEV-ECU connector terminal for open circuit.
(1) Disconnect the connector and the IGCT relay and measure at the harness connector side.
(2) Check the wiring harness between PHEV-ECU connector (terminal CNTB) and the IGCT relay connector.
Is the check result normal?
STEP 3. Check the main drive lithium-ion battery main contactor (P) and (N) <On-vehicle check>.
Check resistance of main contactor (P) and (N) coil with harness connector (Refer to  ).
).
 ).
).Is the check result normal?
STEP 4. Test the OBD-II drive cycle.
(1) Carry out a test drive with the drive cycle pattern. Refer to Diagnostic Function - OBD-II Drive Cycle - Pattern 3  .
.
 .
.(2) Check the DTC.
Is the DTC set?
STEP 5. Check the CNTP wire at the main drive lithium-ion battery connector for short to ground.
Disconnect the connector and check for short to ground circuit.
Is the check result normal?
STEP 6. Check the signal line for short to ground circuit (main drive lithium-ion battery connector and charging contactor).
Check the wiring harness between main drive lithium-ion battery connector (terminal No.1) and the charging contactor (terminal No.4).
Is the check result normal?
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)