BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATION CHECK
INSPECTION WITHOUT USING TESTER
1. Carry out the simplified brake booster operation check in the following procedure:
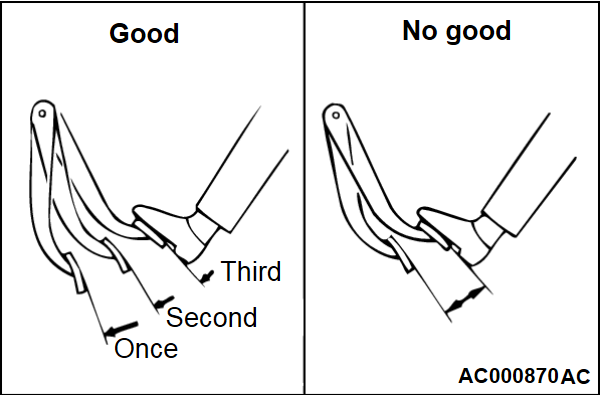
(1) Run the engine for 1 to 2 minutes, and then stop. Depress the brake pedal with normal depression force. The result is judged as "Good" when the pedal stroke is great at the first depression, and becomes smaller as you repeat depressing the pedal. If the pedal stroke does not change, the result is judged as "No Good."
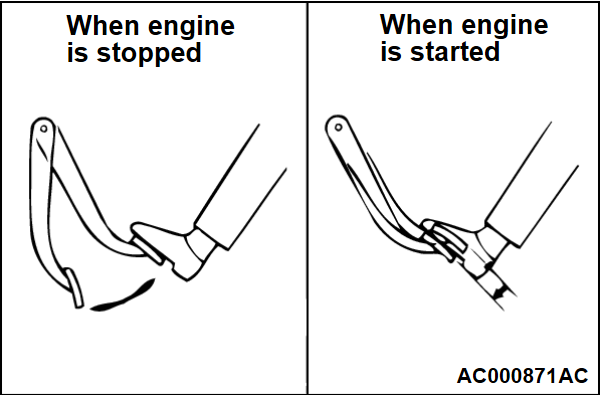
(2) With the engine stopped, depress the brake pedal several times. Keep the brake pedal depressed and start the engine. At this time, when the pedal moves down slightly, the result is judged as "Good." The result is judged as "No Good" if the pedal does not move down.
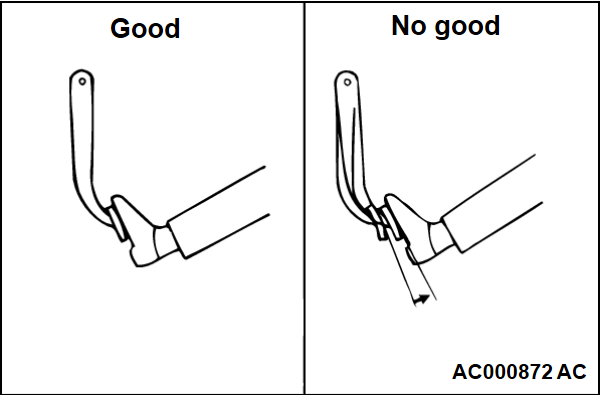
(3) With the engine running, depress the brake pedal. Stop the engine in this condition. The result is judged as "Good" when the pedal height does not change for approximately 30 seconds. The result is judged as "No Good" if the pedal moves up.
2. The brake booster is judged as normal when the results of all the above checks are "Good."
When one or more of the above check results are "No Good", then the check valve, vacuum hose, or brake booster is suspected faulty.
INSPECTION USING SIMPLIFIED TESTER
Required Special Tool:
- MB992146: Booster test adapter installer
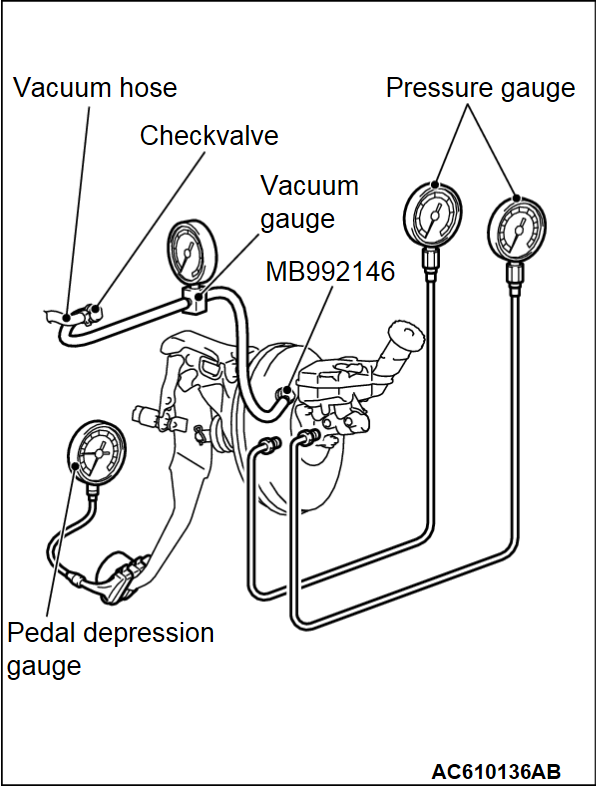
1. Before starting this inspection, remove the brake booster check valve from the vehicle and check its operation (Refer to  ).
).
 ).
).2. After checking, install the check valve to the vacuum hose and connect it to the vacuum gauge. Install the booster test adapter (Special tool: MB992146) to the brake booster and connect it to the vacuum gauge. Connect the pressure gauge and pedal depression gauge as shown in the figure. Bleed the pressure gauge and then perform the following tests:
(1) Airtightness test with no load
Start the engine, and stop it when the vacuum gauge indicator has reached approximately -67 kPa (-9.7 psi). The result is judged as "Good" when the drop of the vacuum approximately 15 seconds after the engine was stopped is within -3.3 kPa (-0.5 psi).
(2) Airtightness test with load
Start the engine and depress the brake pedal with 200 N. Stop the engine when the vacuum gauge indicator reached approximately -67 kPa (-9.7 psi). The result is judged as "Good" when the drop of the vacuum approximately 15 seconds after the engine was stopped is within -3.3 kPa (-0.5 psi).
When one or more of the above check results are judged as "No Good", the vacuum hose or brake booster is suspected faulty.
(3) Brake booster characteristics test
Perform this test after the above (1) and (2) were performed.
.....1. Non-servo effect test
With the engine stopped, make sure that the vacuum gauge reading is 0 kPa (0 psi). Depress the brake pedal with 100 N (22.5 lb) and 300 N (67.4 lb), and measure the fluid pressure generated.
Standard value:
| |||||||||
| Item | Pedal depression force | |
| 100 N (22.5 lb) | 300 N (67.4 lb) | |
| Generated fluid pressure kPa (psi) | 0 - 600 (0 - 87) | 1,030 - 2,220 (149 - 322) |
.....2. Servo effect test
Start the engine. Depress the brake pedal with 100 N (22.5 lb) and 300 N (67.4 lb) when the vacuum gauge indicator reached approximately -67 kPa (-9.7 psi), and measure the fluid pressure generated.
Standard value:
| |||||||||
| Item | Pedal depression force | |
| 100 N (22.5 lb) | 300 N (67.4 lb) | |
| Generated fluid pressure kPa (psi) | 6,570 - 8,330 (953 - 1,208) | 10,370 - 11,560 (1,504 - 1,677) |
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)