COMPRESSION PRESSURE CHECK
1. Before inspection, set the vehicle to the pre-inspection condition.
2. Remove all of the ignition coils and spark plugs.
3. Disconnect the all of the injector connectors.
| caution |
|
4. Cover the spark plug hole with a shop towel etc., and after the engine has been cranked, check that no foreign material is adhering to the shop towel.
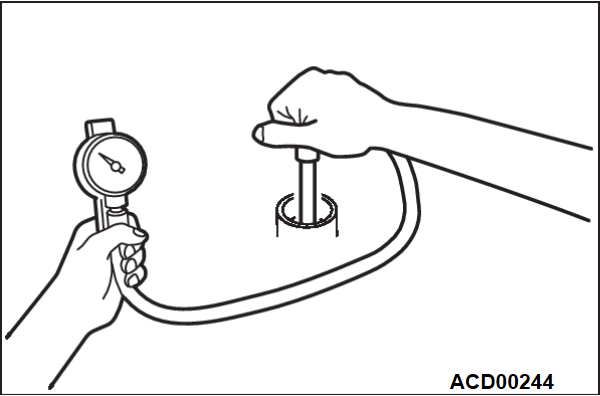
5. Set compression gauge to one of the spark plug holes.
6. Cranking the engine with the accelerator pedal fully depressed, measure the compression pressure.
- Standard value (at engine speed of 250 r/min): 1,330 kPa (193 psi)
- Limit (at engine speed of 250 r/min): Minimum 990 kPa (144 psi)
7. Measure the compression pressure for all the cylinders, and check that the pressure differences of the cylinders are below the limit.
Limit: Maximum 98 kPa (14 psi)
8. If there is a cylinder with compression or a compression difference that is outside the limit, pour a small amount of engine oil through the spark plug hole, and repeat the operations in steps from 5 to 7.
(1) If the compression increases after oil is added, the cause of the malfunction is a worn or damaged piston ring and/or cylinder inner surface.
(2) If the compression does not rise after oil is added, the cause is a burnt or defective valve seat, or pressure is leaking from the gasket.
9. Connect the crank angle sensor connector.
10. Install the spark plugs and spark plug cables.
11. Use the scan tool (M.U.T.-IIISE) to erase the diagnostic trouble codes.
| note | This will erase the diagnostic trouble code resulting from the injector connectors being disconnected. |
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)