|
|
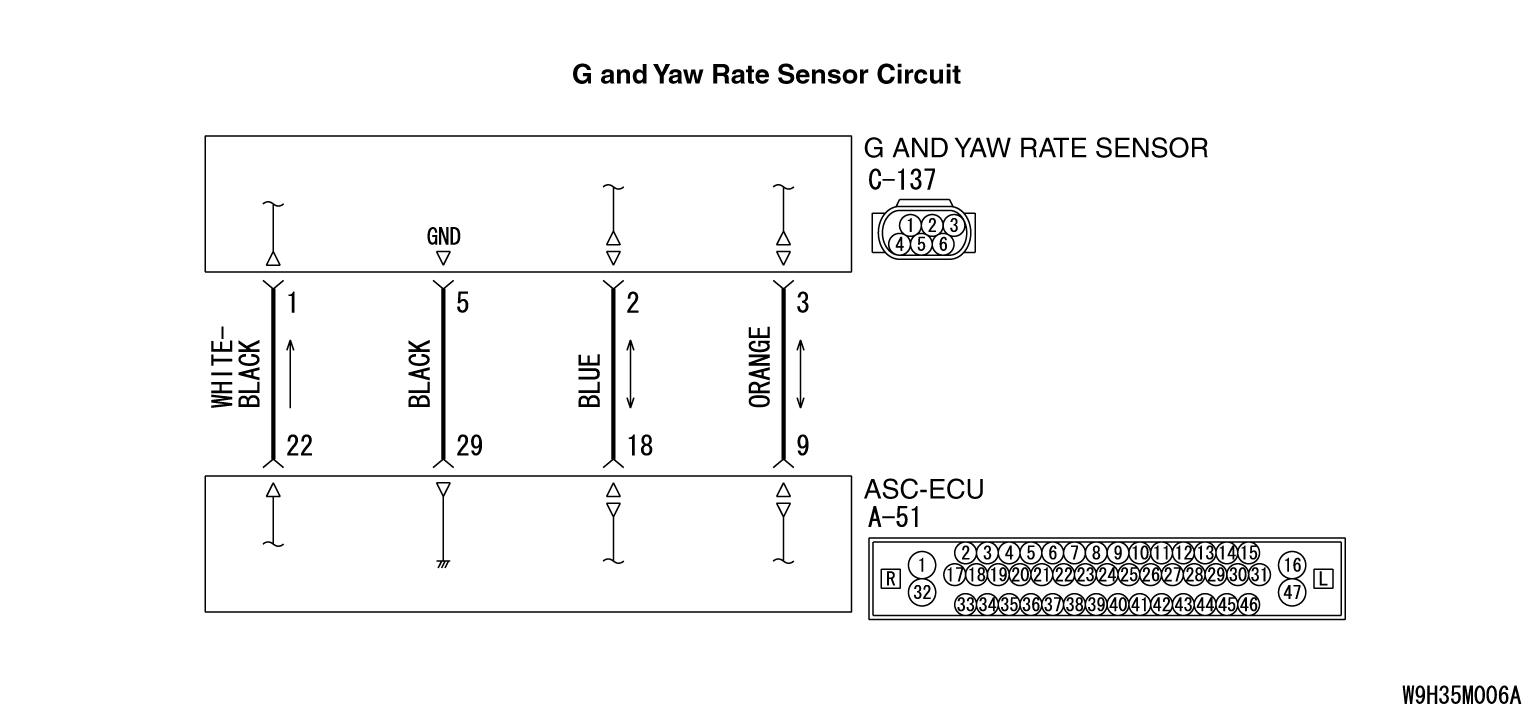
ABS-ECU monitors if the output of G and yaw rate sensor is normal or not.
|
|
|
This DTC is set when the abnormality is detected by comparing the longitudinal G-sensor
value output from the G and yaw rate sensor with the value output from the wheel speed sensor.
|
|
|
- Wiring harness or connector failure for the special CAN bus lines between
ASC-ECU and the G and yaw rate sensor
- Improper installation of the G and yaw rate sensor
- G and yaw rate sensor malfunction
- Malfunction of wheel speed sensor
- ASC-ECU malfunction
- External noise interference
|
|
|
Required Special Tools:
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: Vehicle Communication Interface (V.C.I.)
- MB991827: M.U.T.-III USB Cable
- MB991910: M.U.T.-III Main Harness A
|
|
|
Use scan tool to diagnose the CAN bus lines.
|
|
|
Q.
Is the check result normal?
|
|
|
 Repair the CAN bus lines (Refer to GROUP 54C - CAN Bus Diagnostic table Repair the CAN bus lines (Refer to GROUP 54C - CAN Bus Diagnostic table  ).
On completion, go to Step 2. ).
On completion, go to Step 2.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check that the DTC U0125 is set in ASC-ECU.
|
|
|
 Troubleshoot for the DTC (Refer to Troubleshoot for the DTC (Refer to  ). Then go to
Step 3. ). Then go to
Step 3.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 The procedure is complete. The procedure is complete.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use the scan tool to check whether the wheel speed sensor-related DTC is set or not.
|
|
|
 Troubleshoot for the relevant DTC (Refer to Troubleshoot for the relevant DTC (Refer to  ). ).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check that the G and yaw rate sensor is installed correctly.
|
|
|
Q.
Is the check result normal?
|
|
|
 After checking the G and yaw rate sensor, carry out calibration of the G and yaw
rate sensor to make ASC-ECU relearn the neutral point. (Refer to After checking the G and yaw rate sensor, carry out calibration of the G and yaw
rate sensor to make ASC-ECU relearn the neutral point. (Refer to  .) Then
go to Step 6. .) Then
go to Step 6.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Reinstall the G and yaw rate sensor correctly (Refer to Reinstall the G and yaw rate sensor correctly (Refer to  ),
and then go to Step 10. ),
and then go to Step 10.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check the following service data (Refer to  ). ).
|
|
|
Q.
Is the check result normal?
|
|
|
Q.
Is the check result normal?
|
|
|
 Repair the connector, and then go to Step 10. Repair the connector, and then go to Step 10.
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Check the communication circuit for open and short circuit.
|
|
|
Q.
Is the check result normal?
|
|
|
 Replace the G and yaw rate sensor.(Refer to Replace the G and yaw rate sensor.(Refer to  .) Then
go to Step 9. .) Then
go to Step 9.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Repair the wiring harness, and then go to Step 10. Repair the wiring harness, and then go to Step 10.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2)Drive the vehicle at 12mph (20 km/h) or higher.
|
|
|
 Replace the hydraulic unit (integrated with ASC-ECU) (Refer to Replace the hydraulic unit (integrated with ASC-ECU) (Refer to  ), and
then go to Step 10. ), and
then go to Step 10.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - How to Cope with Intermittent
Malfunction Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - How to Cope with Intermittent
Malfunction  ). ).
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2)Drive the vehicle at 12mph (20 km/h) or higher.
|
|
|
 The procedure is complete. The procedure is complete.
|
|
|
|
![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)
 Go to Step 2.
Go to Step 2. Repair the CAN bus lines (Refer to GROUP 54C - CAN Bus Diagnostic table
Repair the CAN bus lines (Refer to GROUP 54C - CAN Bus Diagnostic table  ).
On completion, go to Step 2.
).
On completion, go to Step 2. Troubleshoot for the DTC (Refer to
Troubleshoot for the DTC (Refer to  ). Then go to
Step 3.
). Then go to
Step 3. Go to Step 3.
Go to Step 3. Go to Step 4.
Go to Step 4. The procedure is complete.
The procedure is complete. Troubleshoot for the relevant DTC (Refer to
Troubleshoot for the relevant DTC (Refer to  ).
). Go to Step 5.
Go to Step 5. After checking the G and yaw rate sensor, carry out calibration of the G and yaw
rate sensor to make ASC-ECU relearn the neutral point. (Refer to
After checking the G and yaw rate sensor, carry out calibration of the G and yaw
rate sensor to make ASC-ECU relearn the neutral point. (Refer to  .) Then
go to Step 6.
.) Then
go to Step 6. Reinstall the G and yaw rate sensor correctly (Refer to
Reinstall the G and yaw rate sensor correctly (Refer to  ),
and then go to Step 10.
),
and then go to Step 10. ).
). Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 9. Go to Step 7.
Go to Step 7. Go to Step 8.
Go to Step 8. Repair the connector, and then go to Step 10.
Repair the connector, and then go to Step 10. Replace the G and yaw rate sensor.(Refer to
Replace the G and yaw rate sensor.(Refer to  .) Then
go to Step 9.
.) Then
go to Step 9. Repair the wiring harness, and then go to Step 10.
Repair the wiring harness, and then go to Step 10. Replace the hydraulic unit (integrated with ASC-ECU) (Refer to
Replace the hydraulic unit (integrated with ASC-ECU) (Refer to  ), and
then go to Step 10.
), and
then go to Step 10. Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - How to Cope with Intermittent
Malfunction
Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - How to Cope with Intermittent
Malfunction  ).
). Return to Step 1.
Return to Step 1. The procedure is complete.
The procedure is complete.