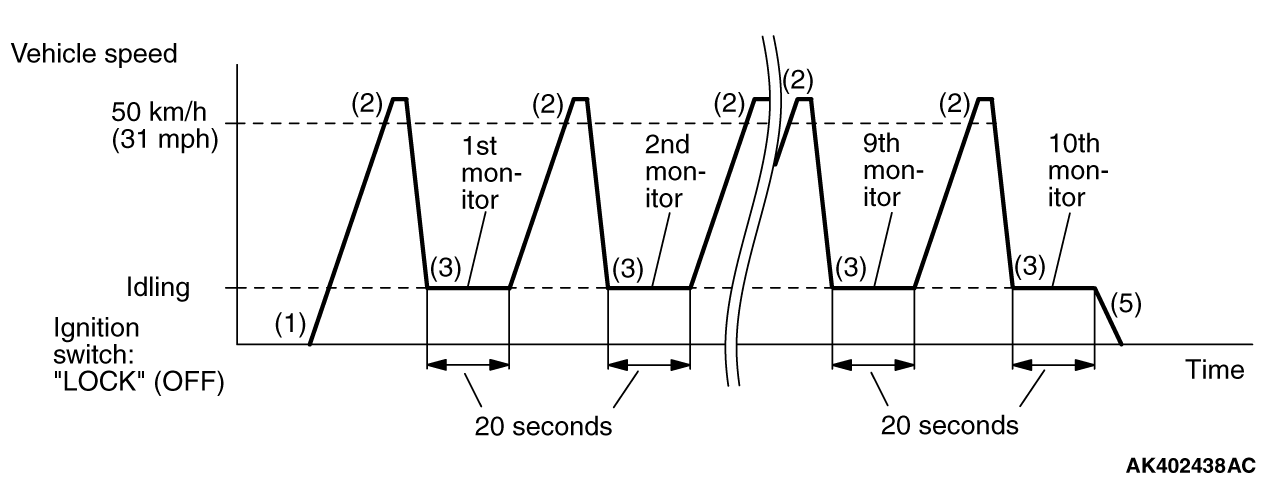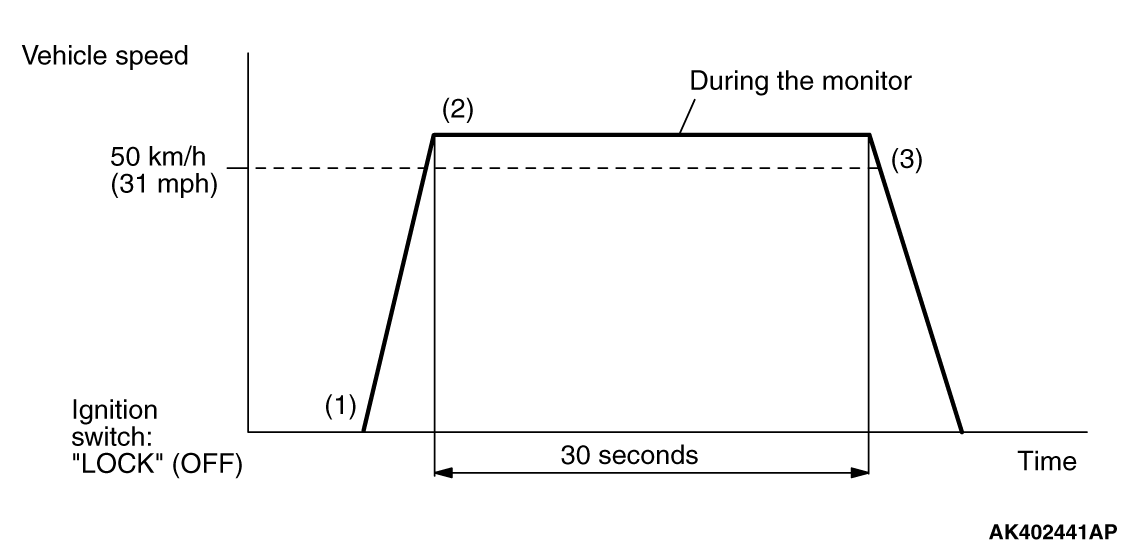
|
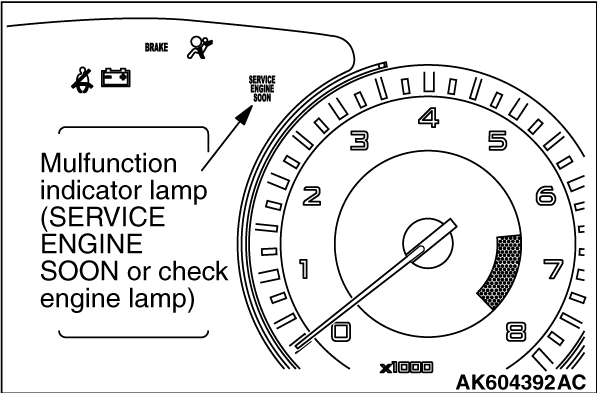
Among the on-board diagnostic items, Malfunction Indicator Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or
Check Engine Lamp) illuminates to notify the driver of an emission control malfunction.
However, when an irregular signal returns to normal and the engine control module judges
that it has returned to normal, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or Check
Engine Lamp) will switch off.
There are two methods for checking the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON
or Check Engine Lamp) burn out: When the ignition switch is in ON position, the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or Check Engine Lamp) is illuminated, and then extinguished few seconds
later. When the ignition switch is in ON position and the engine starts, the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or Check Engine Lamp) is extinguished.
| note |
When the Transmission Control Module (TCM) detects malfunctions related to the CVT, the
Malfunction indicator Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or Check Engine Lamp) is also illuminated.
|
|
DTC
|
ITEM
|
P0010
|
Intake engine oil control valve circuit
|
P0011
|
Intake variable valve timing system target error
|
P0013
|
Exhaust engine oil control valve circuit
|
P0014
|
Exhaust variable valve timing system target error
|
P0016
|
Crankshaft/camshaft (intake) position sensor phase problem
|
P0017
|
Crankshaft/camshaft (exhaust) position sensor phase problem
|
P0031
|
Heated oxygen sensor (front) heater circuit low
|
P0032
|
Heated oxygen sensor (front) heater circuit high
|
P0037
|
Heated oxygen sensor (rear) heater circuit low
|
P0038
|
Heated oxygen sensor (rear) heater circuit high
|
P0069
|
Abnormal correlation between manifold absolute pressure sensor and
barometric pressure sensor
|
P0101*1
|
Mass airflow circuit range/performance problem
|
P0102*1
|
Mass airflow circuit low input
|
P0103*1
|
Mass airflow circuit high input
|
P0106
|
Manifold absolute pressure circuit range/performance problem
|
P0107
|
Manifold absolute pressure circuit low input
|
P0108
|
Manifold absolute pressure circuit high input
|
P0111*1
|
Intake air temperature circuit range/performance problem
|
P0112*1
|
Intake air temperature circuit low input
|
P0113*1
|
Intake air temperature circuit high input
|
P0116*1
|
Engine coolant temperature circuit range/performance problem
|
P0117*1
|
Engine coolant temperature circuit low input
|
P0118*1
|
Engine coolant temperature circuit high input
|
P0122*1
|
Throttle position sensor (main) circuit low input
|
P0123*1
|
Throttle position sensor (main) circuit high input
|
P0125*1
|
Insufficient coolant temperature for closed loop fuel control
|
P0128
|
Coolant thermostat (coolant temperature below thermostat regulating
temperature)
|
P0131
|
Heated oxygen sensor (front) circuit low voltage
|
P0132
|
Heated oxygen sensor (front) circuit high voltage
|
P0133
|
Heated oxygen sensor (front) circuit slow response
|
P0134*1
|
Heated oxygen sensor (front) circuit no activity detected
|
P0137
|
Heated oxygen sensor (rear) circuit low voltage
|
P0138
|
Heated oxygen sensor (rear) circuit high voltage
|
P0139
|
Heated oxygen sensor (rear) circuit slow response
|
P0140
|
Heated oxygen sensor (rear) circuit no activity detected
|
P0171
|
System too lean
|
P0172
|
System too rich
|
P0181
|
Fuel tank temperature sensor circuit range/performance
|
P0182
|
Fuel tank temperature sensor circuit low input
|
P0183
|
Fuel tank temperature sensor circuit high input
|
P0201
|
Injector circuit - cylinder 1
|
P0202
|
Injector circuit - cylinder 2
|
P0203
|
Injector circuit - cylinder 3
|
P0204
|
Injector circuit - cylinder 4
|
P0222*1
|
Throttle position sensor (sub) circuit low input
|
P0223*1
|
Throttle position sensor (sub) circuit high input
|
P0300*2
|
Random/multiple cylinder misfire detected
|
P0301*2
|
Cylinder 1 misfire detected
|
P0302*2
|
Cylinder 2 misfire detected
|
P0303*2
|
Cylinder 3 misfire detected
|
P0304*2
|
Cylinder 4 misfire detected
|
P0327
|
Knock sensor circuit low
|
P0328
|
Knock sensor circuit high
|
P0335*1
|
Crankshaft position sensor circuit
|
P0340*1
|
Intake camshaft position sensor circuit
|
P0365*1
|
Exhaust camshaft position sensor circuit
|
P0401
|
Exhaust gas recirculation flow insufficient detected
|
P0420
|
Warm up catalyst efficiency below threshold
|
P0441
|
Evaporative emission control system incorrect purge flow
|
P0442
|
Evaporative emission control system leak detected (small leak)
|
P0443
|
Evaporative emission control system purge control valve circuit
|
P0446
|
Evaporative emission control system vent control circuit
|
P0450
|
Evaporative emission control system pressure sensor malfunction
|
P0451
|
Evaporative emission control system pressure sensor range/performance
|
P0452
|
Evaporative emission control system pressure sensor low input
|
P0453
|
Evaporative emission control system pressure sensor high input
|
P0455
|
Evaporative emission control system leak detected (gross leak)
|
P0456
|
Evaporative emission control system leak detected (very small leak)
|
P0461
|
Fuel level sensor circuit range/performance
|
P0462
|
Fuel level sensor circuit low input
|
P0463
|
Fuel level sensor circuit high input
|
P0489
|
EGR valve (stepper motor) circuit malfunction (ground short)
|
P0490
|
EGR valve (stepper motor) circuit malfunction (battery short)
|
P0500*1
|
Vehicle speed sensor malfunction <M/T>
|
P0506
|
Idle control system RPM lower than expected
|
P0507
|
Idle control system RPM higher than expected
|
P050B
|
Ignition timing retard insufficient
|
P0551
|
Power steering pressure switch circuit range/performance
|
P0554
|
Power steering pressure switch circuit intermittent
|
P0603*1
|
EEPROM malfunction
|
P0606*1
|
Engine control module main processor malfunction
|
P0630*1
|
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) malfunction
|
P0638*1
|
Throttle actuator control motor circuit range/ performance
|
P0642*1
|
Throttle position sensor power supply
|
P0657*1
|
Throttle actuator control motor relay circuit malfunction
|
P1233*1
|
Throttle position sensor (main) plausibility
|
P1234*1
|
Throttle position sensor (sub) plausibility
|
P1235*1
|
Mass airflow sensor plausibility
|
P1236*1
|
A/D converter
|
P1237*1
|
Accelerator pedal position sensor plausibility
|
P1238*1
|
Mass airflow sensor plausibility (torque monitor)
|
P1239*1
|
Engine RPM plausibility
|
P1241*1
|
Torque monitor
|
P1506
|
Idle control system RPM lower than expected at low temperature
|
P1507
|
Idle control system RPM higher than expected at low temperature
|
P1590*1
|
TCM to ECM communication error in torque reduction request <CVT>
|
P1603*1
|
Battery backup circuit malfunction
|
P1676*1
|
Variant coding
|
P2100*1
|
Throttle actuator control motor circuit (open)
|
P2101*1
|
Throttle actuator control motor magneto malfunction
|
P2122*1
|
Accelerator pedal position sensor (main) circuit low input
|
P2123*1
|
Accelerator pedal position sensor (main) circuit high input
|
P2127*1
|
Accelerator pedal position sensor (sub) circuit low input
|
P2128*1
|
Accelerator pedal position sensor (sub) circuit high input
|
P2135*1
|
Throttle position sensor (main and sub) range/performance problem
|
P2138*1
|
Accelerator pedal position sensor (main and sub) range/performance
problem
|
P2195
|
Heated oxygen sensor (front) inactive
|
P2228*1
|
Barometric pressure circuit low input
|
P2229*1
|
Barometric pressure circuit high input
|
P2252
|
Heated oxygen sensor offset circuit low voltage
|
P2253
|
Heated oxygen sensor offset circuit high voltage
|
U0101*1
|
TCM time-out <CVT>
|
U0141*1
|
ETACS-ECU time-out
|
U1180*1
|
Combination meter time-out
|
|
|
Required Special Tools:
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: V.C.I.
- MB991827: USB Cable
- MB991910: Main Harness A
|
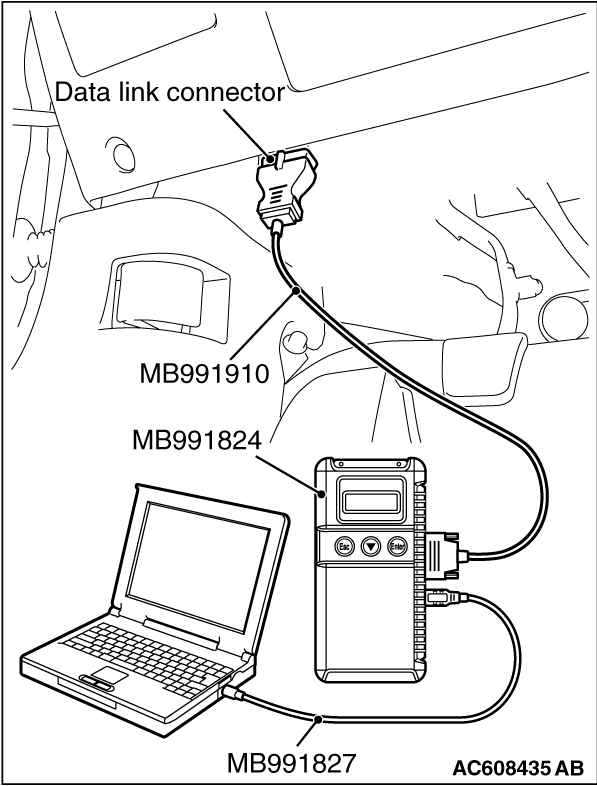
|
1.Ensure that the ignition switch is at the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
2.Start up the personal computer.
3.Connect special tool MB991827 to special tool MB991824 and the personal computer.
4.Connect special tool MB991910 to special tool MB991824.
5.Connect special tool MB991910 to the data link connector.
6.Turn the power switch of special tool MB991824 to the "ON" position.
| note |
When the special tool MB991824 is energized, special tool MB991824 indicator light will
be illuminated in a green color.
|
7.Start the M.U.T.-III system on the personal computer.
| note |
Disconnecting the scan tool MB991958 is the reverse of the connecting sequence, making
sure that the ignition switch is at the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
|
|
|
|
Required Special Tools:
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: V.C.I.
- MB991827: USB Cable
- MB991910: Main Harness A
|

|
1.Connect scan tool MB991958 to the data link connector.
2.Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
3.Select "System select."
4.Choose "from 2006 MY" under "MODEL YEAR".
5.Check that "Vehicle Information" contents are correct.
6.Choose "MFI".
7.Select "Diagnostic Trouble Code"
8.If a DTC is set, it is shown.
9.Choose "Erase DTCs" to erase the DTC.
|
|
|
Required Special Tools:
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: V.C.I.
- MB991827: USB Cable
- MB991910: Main Harness A
|

|
1.Connect scan tool MB991958 to the data link connector.
2.Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
3.Select "System select."
4.Choose "from 2006 MY" under "MODEL YEAR".
5.Check that "Vehicle Information" contents are correct.
6.Choose "MFI".
7.Select "Data List."
8.Choose an appropriate item and select the "OK" button.
|
|
|
Required Special Tools:
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: V.C.I.
- MB991827: USB Cable
- MB991910: Main Harness A
|

|
1.Connect scan tool MB991958 to the data link connector.
2.Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
3.Select "System select."
4.Choose "from 2006 MY" under "MODEL YEAR".
5.Check that "Vehicle Information" contents are correct.
6.Choose "MFI".
7.Select "Actuator Test."
8.Choose an appropriate item and select the "OK" button.
|
|
|
Required Special Tools:
- MB991958: Scan Tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: V.C.I.
- MB991827: USB Cable
- MB991910: Main Harness A
|

|
1.Connect scan tool MB991958 to the data link connector.
2.Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
3.Select "CAN bus diagnosis" from the start-up screen.
4.When the vehicle information is displayed, confirm that it matches the vehicle whose
CAN bus lines will be diagnosed.
- If they matches, go to step 8.
- If not, go to step 5.
5.Select the "view vehicle information" button.
6.Enter the vehicle information and select the "OK" button.
7.When the vehicle information is displayed, confirm again that it matches the vehicle
whose CAN bus lines will be diagnosed.
- If they matches, go to step 8.
- If not, go to step 5.
8.Select the "OK" button.
9.When the optional equipment screen is displayed, choose the one which the vehicle
is fitted with, and then select the "OK" button.
|
|
|
The general scan tool will display the Provisional DTCs reported by ECM
if the ECM detects some malfunction for "Misfire", "Fuel System" and "Comprehensive" monitoring during
a SINGLE Driving Cycle. The intended use of this data is to assist the technician after a vehicle
repair, and after clearing diagnostic information, by reporting test result after a SINGLE Driving
Cycle. Note that the test results reported by this mode do not necessarily indicate a faulty
component/system. If test results indicate a failure after ADDITIONAL (consecutive) driving,
then the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON or Check Engine Lamp) will be illuminated
and a DTC will set.
|
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC MONITOR ID
|
STANDARDIZED / MANUFACTURER DEFIND TEST ID
|
MONITORING ITEM
|
SIMPLE TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
|
CONVERSION COEFFICIENT IN USING GENERAL SCAN TOOL
|
01
|
81
|
Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 1
Rich/Lean Switching frequency
|
ECM monitors the deteriorated condition of the heated oxygen sensor (front)
by checking the rich/lean switching frequency of the heated oxygen sensor (front).
|
× 1 count
|
02
|
08
|
Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 2
Maximum Sensor Voltage for Test Cycle
|
PCM checks the output voltage of the cylinder 1, 4 heated oxygen
sensor (rear) in order to monitor whether the cylinder 1, 4 heated oxygen sensor (rear) outputs
the rich signal.
|
× 0.122mV
|
82
|
Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 2
Output Voltage change
|
ECM checks the output voltage of the heated oxygen sensor (rear)
in order to monitor whether the heated oxygen sensor (rear) output is stuck.
|
× 0.122 mV
|
05
|
Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 2
Rich To Lean Sensor Switch Time
|
ECM checks the rich to lean switching time of the heated oxygen sensor
(rear) in order to monitor the response of the heated oxygen sensor (rear).
|
× 1 msec
|
88
|
Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 2
Output Voltage drop slope
|
ECM checks the output voltage drop slope of the heated oxygen sensor (rear)
in order to monitor the response of the heated oxygen sensor.
|
× 1 msec
|
21
|
83
|
Catalyst Monitor Bank 1
Frequency ratio between Front- and Rear-Oxygen Sensors
|
ECM monitors the deterioration of catalyst by the output frequency
ratio between heated oxygen sensor (front) and heated oxygen sensor (rear).
|
× 0.0039
|
31
|
84
|
EGR Monitor
Difference of manifold pressure before and after EGR activation
|
ECM monitors the operation of EGR system by the pressure difference of
intake manifold between before and after introduction of EGR using the manifold absolute pressure
sensor.
|
× 0.0117 kPa
|
39
|
85
|
EVAP Monitor (Cap off)
Pressure drop during de-pressurizing
|
ECM monitors the leak of fuel evaporation gas by checking whether
the pressure can be reduced (the amount of pressure reduction) using the fuel tank differential
pressure sensor after sealing the fuel tank and the fuel line.
|
× 0.0117 kPa
|
3B
|
85
|
EVAP Monitor (0.040")
Pressure rise during airtight condition
|
After ECM vacuumizes the fuel tank and the fuel line and then the
specified time is passed, ECM monitors the leak of fuel evaporation gas through the fuel tank differential
pressure sensor to check the reduction of vacuum in the fuel tank.
|
× 0.0117 kPa
|
3C
|
85
|
EVAP Monitor (0.020")
Pressure rise during airtight condition
|
After ECM vacuumizes the fuel tank and the fuel line and then the
specified time is passed, ECM monitors the leak of fuel evaporation gas through the fuel tank differential
pressure sensor to check the reduction of vacuum in the fuel tank.
|
× 0.0117 kPa
|
A1
|
0B
|
Mis-Fire General Data
EWMA Misfire Counts For Last 10 Driving Cycles
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
EWMA (Exponential Weighted Moving Average) misfire counts for last 10 driving cycles.
|
× 1 count
|
0C
|
Mis-Fire General Data
Misfire Counts For Last/Current Driving Cycle
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle.
|
× 1 count
|
A2
|
0B
|
Mis-Fire Cylinder 1 Data
EWMA Misfire Counts For Last 10 Driving Cycles
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
EWMA (Exponential Weighted Moving Average) misfire counts for last 10 driving cycles.
|
× 1 count
|
0C
|
Mis-Fire Cylinder 1 Data
Misfire Counts For Last/Current Driving Cycle
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle.
|
× 1 count
|
A3
|
0B
|
Mis-Fire Cylinder 2 Data
EWMA Misfire Counts For Last 10 Driving Cycles
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
EWMA (Exponential Weighted Moving Average) misfire counts for last 10 driving cycles.
|
× 1 count
|
0C
|
Mis-Fire Cylinder 2 Data
Misfire Counts For Last/Current Driving Cycle
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle.
|
× 1 count
|
A4
|
0B
|
Mis-Fire Cylinder 3 Data
EWMA Misfire Counts For Last 10 Driving Cycles.
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
EWMA (Exponential Weighted Moving Average) misfire counts for last 10 driving cycles.
|
× 1 count
|
0C
|
Mis-Fire Cylinder 3 Data
Misfire Counts For Last/Current Driving Cycle
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle.
|
× 1 count
|
A5
|
0B
|
Mis-Fire Cylinder 4 Data
EWMA Misfire Counts For Last 10 Driving Cycles
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
EWMA (Exponential Weighted Moving Average) misfire counts for last 10 driving cycles.
|
× 1 count
|
0C
|
Mis-Fire Cylinder 4 Data
Misfire Counts For Last/Current Driving Cycle
|
ECM monitors angular acceleration of crankshaft and detect misfire.
Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle.
|
× 1 count
|
|
|
Required Special Tools:
- MB991958: Scan tool (M.U.T.-III Sub Assembly)
- MB991824: V.C.I.
- MB991827: USB Cable
- MB991910: Main Harness A
|

|
| caution |
To prevent damage to scan tool MB991958, always turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK"
(OFF) position before connecting or disconnecting scan tool MB991958.
|
| note |
When mode II is selected with MB991958, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE
SOON or Check Engine Lamp) will light when the engine control module (ECM) first detects the
trouble (Note that this is only for emission-related trouble). At the same time, the relevant diagnostic
trouble codes will be registered. In respect to the comprehensive component electrical faults
(opens/shorts), the time for the diagnostic trouble code to be registered after the
fault occurrence is four seconds → one second. Therefore, the confirmation of the trouble
symptom and the confirmation after completing repairs can be reduced. To return to the normal
mode I after mode II has been selected once, the ignition switch must be turned "OFF" once or
mode I must be reselected with the scan tool MB991958. The diagnostic trouble code, system readiness
test status and freeze frame data, etc., will be erased when mode I is returned to, so record
these before returning to mode I.
|
1.Connect scan tool MB991958 to the data link connector.
2.Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position.
3.Change the diagnostic test mode of the engine control module to DIAGNOSTIC TEST MODE
II (INCREASED SENSITIVITY).
4.Road test the vehicle.
5.Read the diagnostic trouble code and repair the malfunctioning part.
6.Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
7.Disconnect scan tool MB991958 from the data link connector.
|
ITEM NO.
|
M.U.T.-III SCAN TOOL DISPLAY
|
DATA ITEM
|
UNIT or STATE
|
AA
|
Airflow sensor
|
Mass airflow sensor
|
g/s
|
AB
|
TP sensor (main)
|
Throttle position sensor (main)
|
%
|
BA
|
Target EGR
|
Target EGR stepper motor
|
%
|
BB
|
Barometric pressure sensor
|
Barometric pressure sensor
|
kPa or in.Hg
|
BC
|
Relative TP sensor
|
Relative throttle position sensor
|
%
|
BD
|
TP sensor (sub)
|
Throttle position sensor (sub)
|
%
|
BE
|
APP sensor (main)
|
Accelerator pedal position sensor (main)
|
%
|
BF
|
APP sensor (sub)
|
Accelerator pedal position sensor (sub)
|
%
|
C0
|
Fuel system status (bank1)
|
Fuel system status
|
|
|
- Open loop-drive condition
|
|
- Closed loop-O2 (rear) failed
|
C2
|
Calculated load value
|
Calculated load value
|
%
|
C3
|
ECT sensor
|
Engine coolant temperature sensor
|
°C or °F
|
C4
|
Short term fuel trim (bank 1)
|
Short term fuel trim
|
%
|
C5*
|
Short term fuel trim (bank 3)
|
Short term fuel trim (bank3)
|
****
|
C6
|
Long term fuel trim (bank 1)
|
Long term fuel trim
|
%
|
C7*
|
Long term fuel trim (bank 3)
|
Long term fuel trim (bank3)
|
****
|
CC
|
MAP sensor
|
Manifold absolute pressure sensor
|
kPa or in.Hg
|
CD
|
Crankshaft position sensor
|
Crankshaft position sensor
|
r/min
|
CE
|
Vehicle speed
|
Vehicle speed
|
km/h or mph
|
CF
|
Spark advance
|
Spark advance
|
°CA
|
D0
|
Intake air temperature sensor
|
Intake air temperature sensor
|
°C or °F
|
D1
|
Time since engine running
|
Time since engine running
|
sec
|
D6
|
EVAP. emission purge SOL. duty
|
Evaporative emission purge solenoid duty
|
%
|
D7
|
Fuel level gauge
|
Fuel level gauge
|
%
|
D8
|
Power supply voltage
|
Power supply voltage
|
V
|
D9
|
Absolute load value
|
Absolute load value
|
%
|
DA
|
Target equivalence ratio
|
Target equivalence ratio
|
-
|
DB
|
Intake air temperature sensor
|
Intake air temperature sensor
|
°C or °F
|
DC
|
Throttle actuator
|
Throttle actuator control motor
|
%
|
COMMON EXAMPLE of GENERAL SCAN TOOL DISPLAY
|
PRAMETER IDENTIFICATION (PID)
|
DESCRIPTION
|
UNIT or STATE
|
DTCFRZF
|
02
|
DTC that caused required freeze frame data storage
|
Pxxxx, Uxxxx
|
FUELSYS 1
|
03
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. C0
|
LOAD_PCT
|
04
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. C2
|
ECT
|
05
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. C3
|
SHRTFT 1
|
06
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. C4
|
LONGFT 1
|
07
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. C6
|
MAP
|
0B
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. CC
|
RPM
|
0C
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. CD
|
VSS
|
0D
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. CE
|
SPARKADV
|
0E
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. CF
|
IAT
|
0F
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. D0
|
MAF
|
10
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. AA
|
TP
|
11
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. AB
|
RUNTM
|
1F
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. D1
|
EGR_PCT
|
2C
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. BA
|
EVAP_PCT
|
2E
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. D6
|
FLI
|
2F
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. D7
|
BARO
|
33
|
See M.U.T.-III Item No. BB
|
VPWR
|
42
|
Control module voltage
|
V
|
LOAD_ABS
|
43
|
Absolute Load Value
|
%
|
EQ_RAT
|
44
|
Commanded Equivalence Ratio
|
%
|
TP_R
|
45
|
Relative Throttle Position
|
%
|
AAT
|
46
|
Ambient air temperature
|
°C (°F)
|
TP_B
|
47
|
Absolute Throttle Position B
|
%
|
APP_D
|
49
|
Accelerator pedal position D
|
%
|
APP_E
|
4A
|
Accelerator pedal position E
|
%
|
TAC_PCT
|
4C
|
Command Throttle Actuator Control
|
%
|
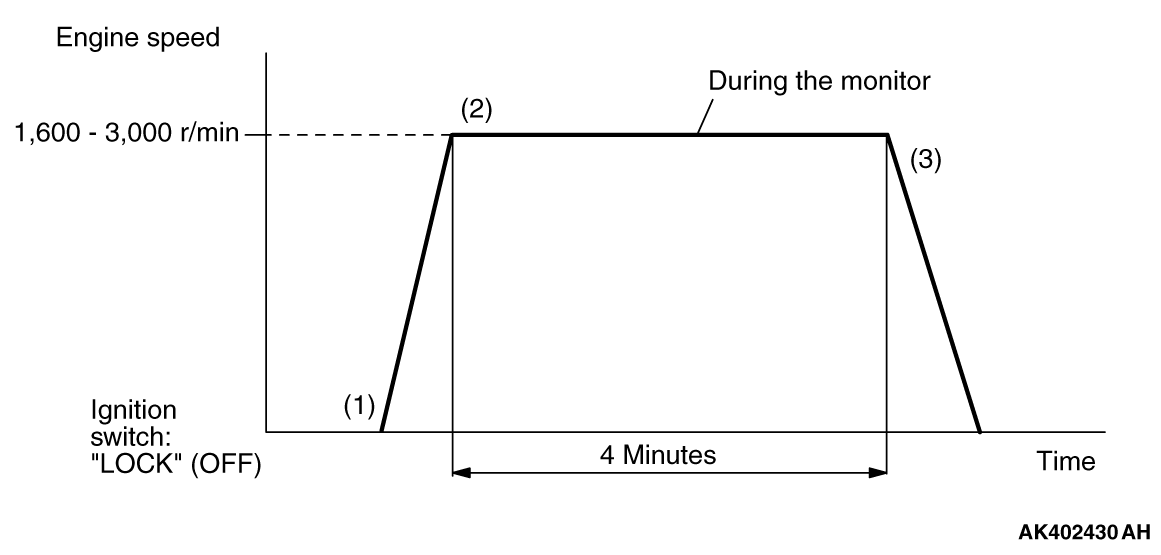
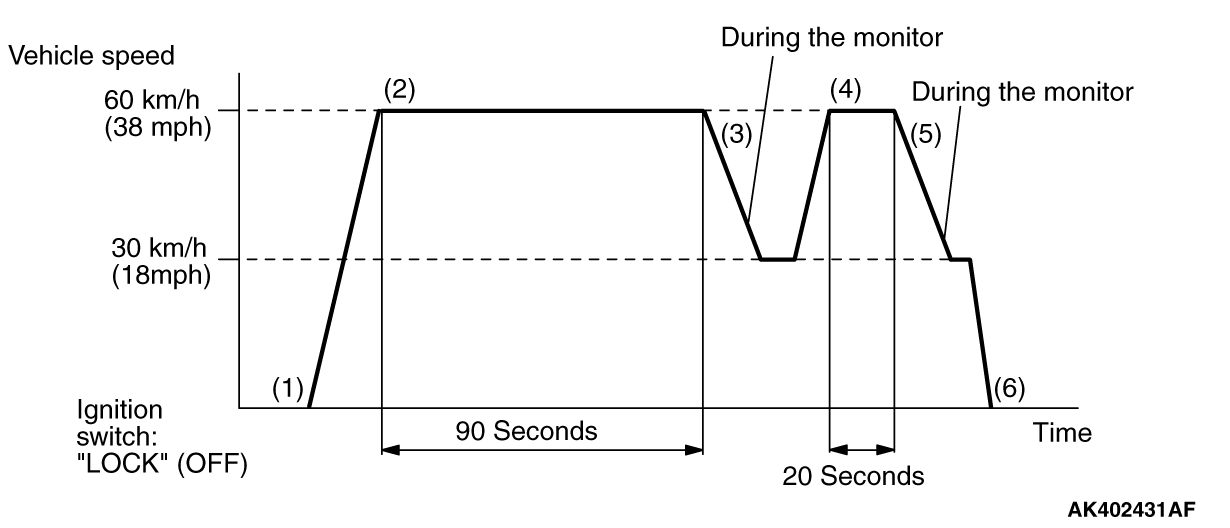
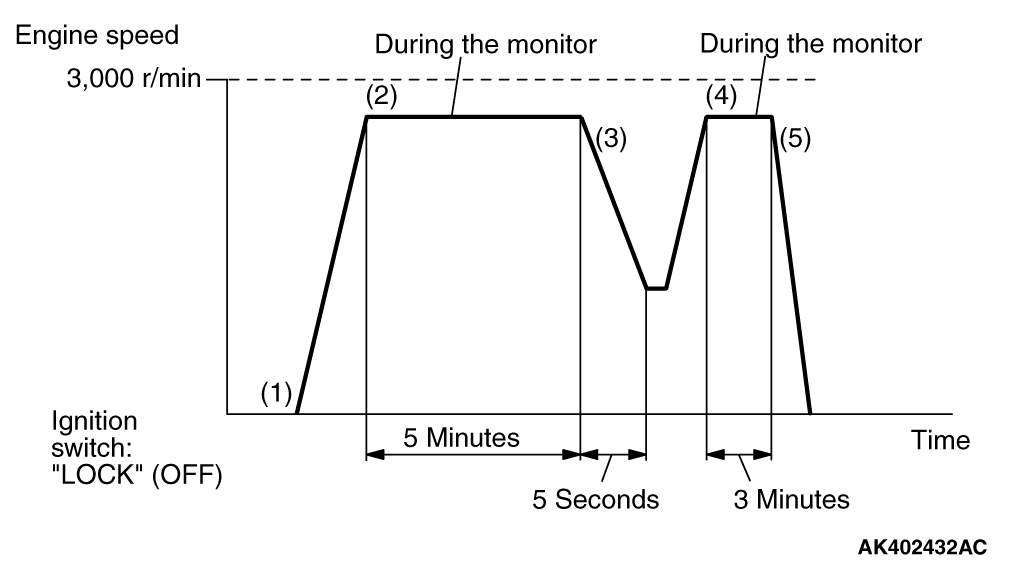
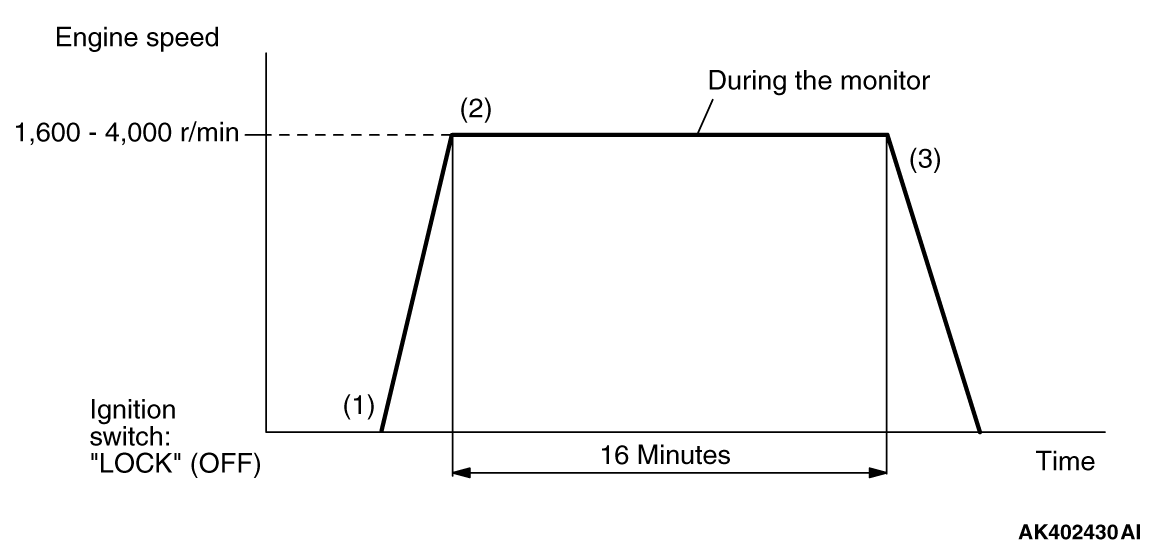
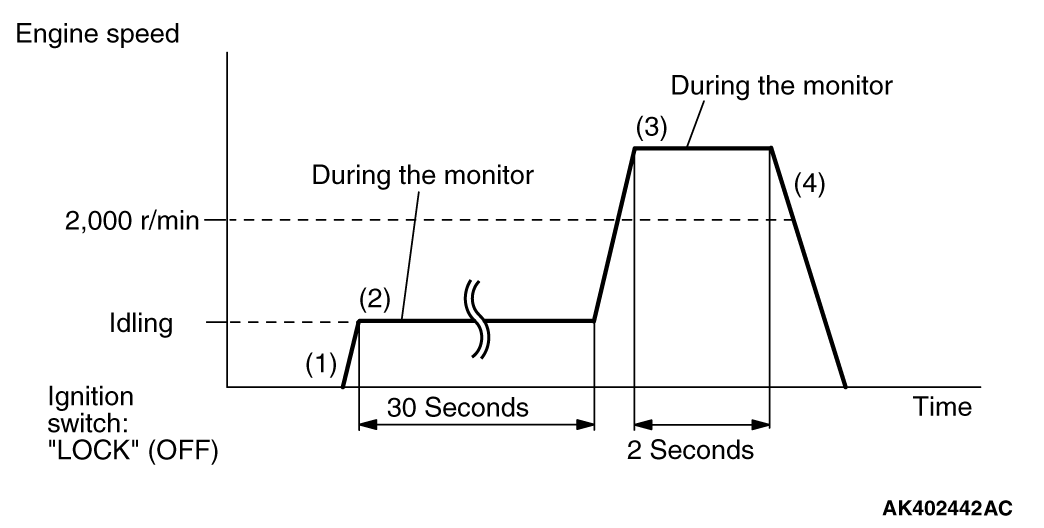
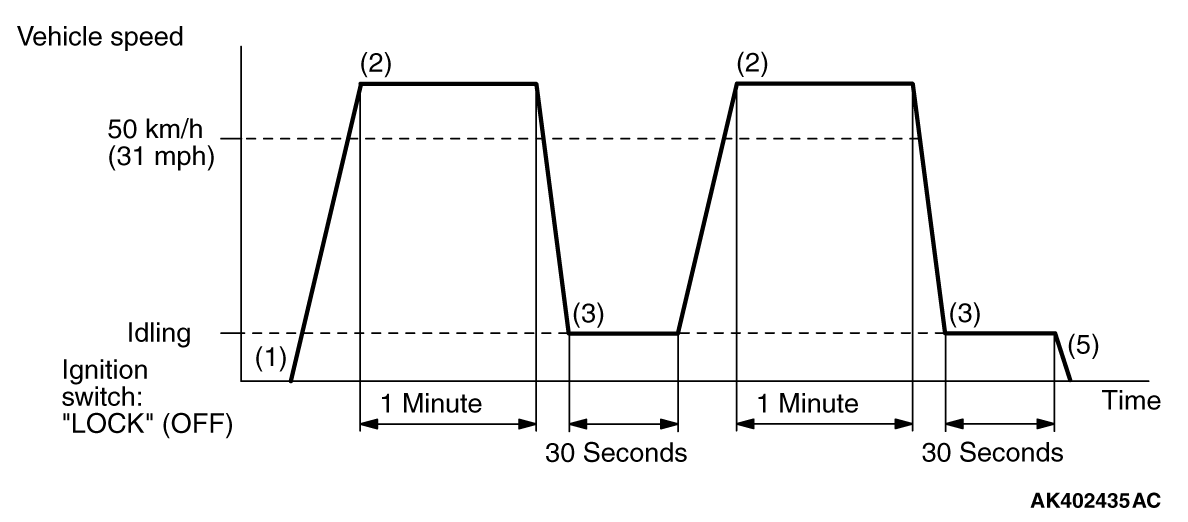
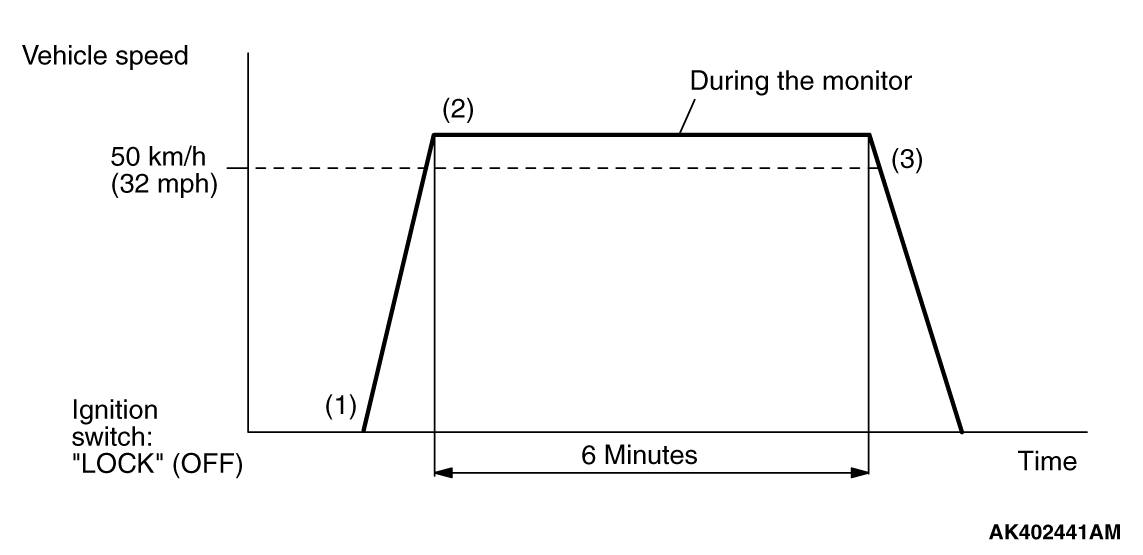
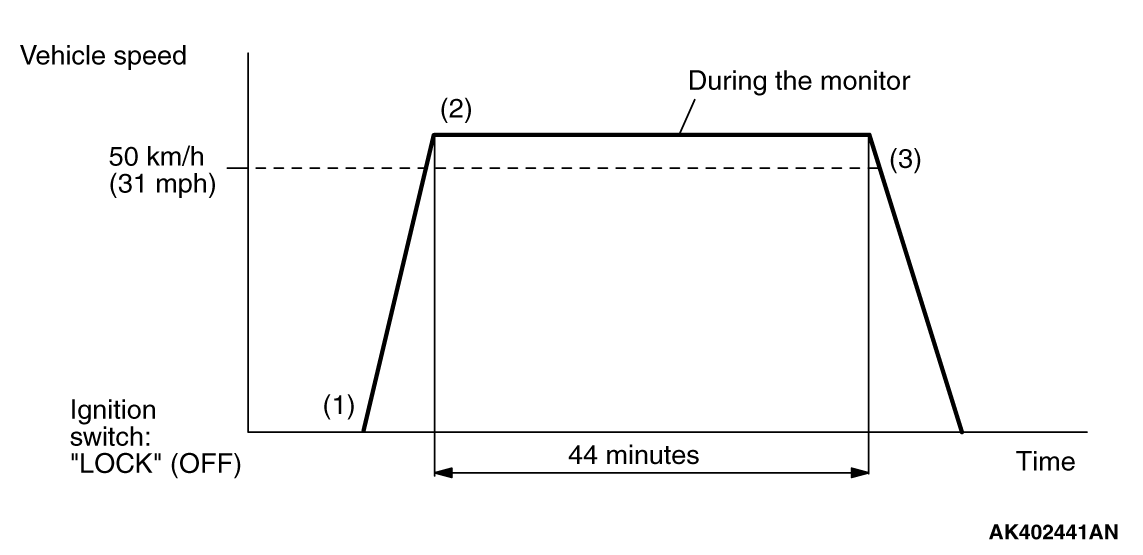
MONITOR ITEM
|
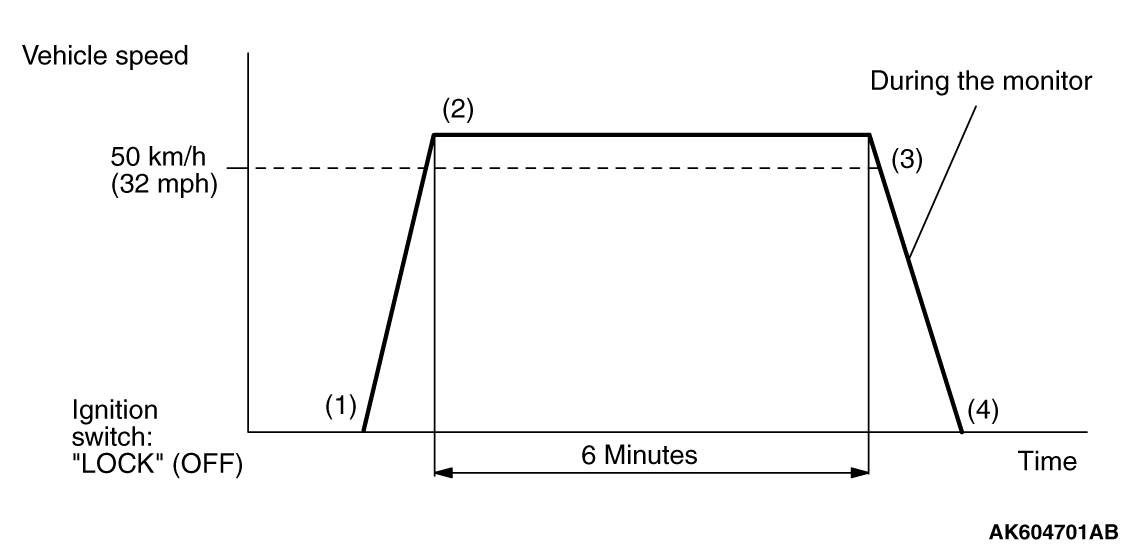
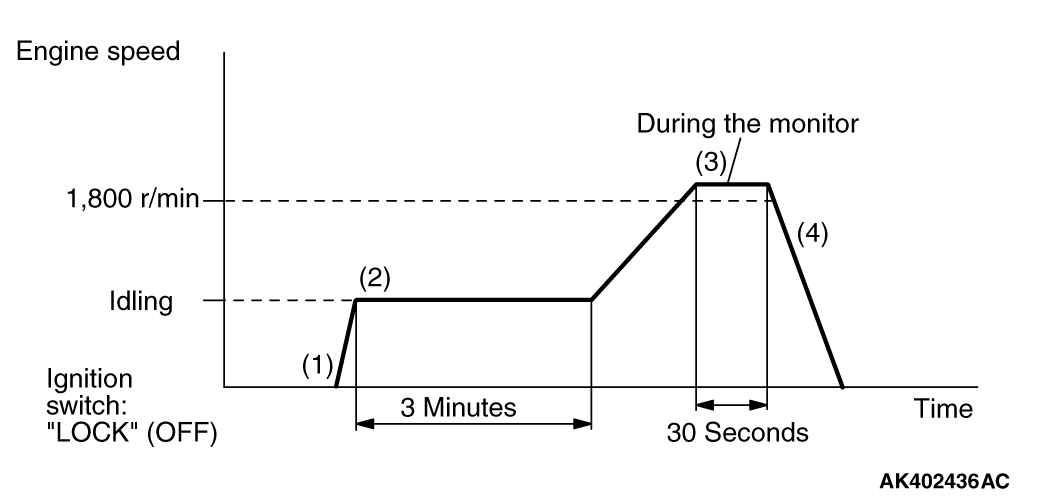
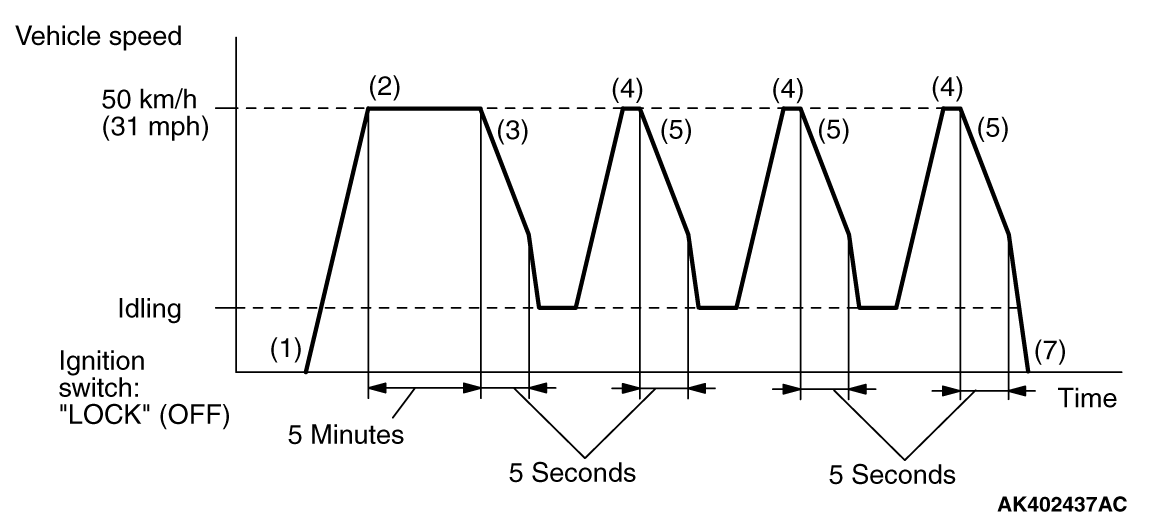
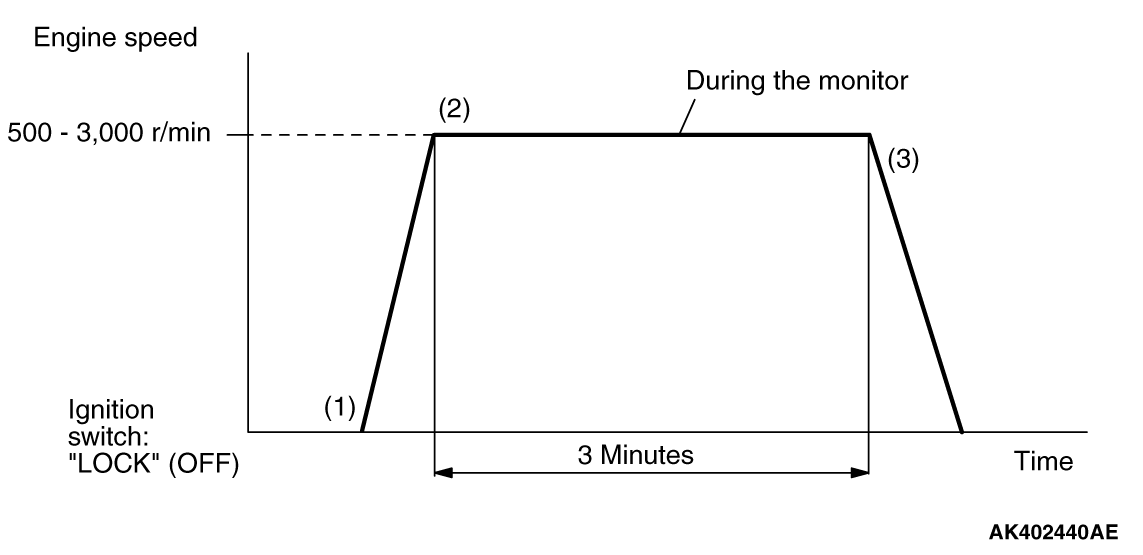
|
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC)
|
PATTERN
|
Heated oxygen sensor (front) monitor <Readiness
test item>
|
P0133
|
1
|
Heated oxygen sensor heater monitor <Readiness
test item>
|
P0031, P0032, P0037, P0038
|
2
|
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system monitor <Readiness
test item>
|
P0401, P0489, P0490
|
3
|
Catalytic converter monitor <Readiness test
item>
|
P0420
|
4
|
Evaporative emission system leak monitor (small leak
and gross leak) <Readiness test item>
|
P0442, P0455
|
5
|
Evaporative purge system monitor
|
P0441
|
|
Fuel tank pressure sensor monitor
|
P0450
|
|
Evaporative emission system leak monitor (very small
leak) <Readiness test item>
|
P0456
|
6
|
Mass airflow sensor monitor
|
P0101
|
7
|
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor monitor
|
P0106, P0107
|
|
Intake air temperature sensor monitor
|
P0111
|
8
|
Engine coolant temperature sensor monitor
|
P0116, P0125
|
9
|
Thermostat monitor
|
P0128
|
10
|
Heated oxygen sensor (rear) monitor <Readiness test item>
|
P0139
|
11
|
Air fuel ratio feedback monitor
|
P0134
|
12
|
Heated oxygen sensor (rear) monitor
|
P0140
|
13
|
Fuel tank temperature sensor monitor
|
P0181
|
14
|
Misfire monitor
|
|
P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304
|
15
|
Fuel tank pressure sensor monitor
|
P0451
|
16
|
Power steering pressure switch monitor
|
P0554
|
17
|
Throttle position sensor plausibility monitor
|
P1233, P1234
|
Mass airflow sensor plausibility monitor
|
P1235, P1238
|
Torque monitor
|
P1241
|
Idle speed control system monitor
|
P0506, P0507
|
18
|
Ignition timing retard control (cold start strategy)
monitor
|
P050B
|
19
|
Idle speed control system monitor
|
P1506, P1507
|
Variable valve timing system (MIVEC) monitor
|
P0011, P0014, P0016, P0017, P1021, P1025
|
20
|
Fuel trim monitor
|
|
P0171, P0172
|
21
|
Heated oxygen sensor monitor
|
P0131, P0137, P2195
|
22
|
Engine oil control valve monitor
|
P0010, P0013
|
23
|
Mass airflow sensor monitor
|
|
P0102, P0103
|
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor monitor
|
P0108
|
Intake air temperature sensor monitor
|
P0112, P0113
|
Engine coolant temperature sensor monitor
|
P0117, P0118
|
Heated oxygen sensor monitor
|
P0132, P0138, P2252, P2253
|
Fuel tank temperature sensor monitor
|
P0182, P0183
|
Injector monitor
|
|
P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204
|
Knock sensor monitor
|
P0327, P0328
|
Crankshaft position sensor monitor
|
P0335
|
Camshaft position sensor monitor
|
P0340, P0365
|
Evaporative emission purge solenoid monitor
|
P0443
|
Evaporative emission ventilation solenoid monitor
|
P0446
|
Fuel tank pressure sensor monitor
|
P0452, P0453
|
Fuel level sensor monitor
|
|
P0462, P0463
|
Engine RPM plausibility monitor
|
P1239
|
Barometric pressure sensor monitor
|
P2228, P2229
|

![[Previous]](../../../buttons/fprev.png)
![[Next]](../../../buttons/fnext.png)